Page 26 - Intelligent Communication Systems
P. 26
I 0 INTELLIGENT COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS
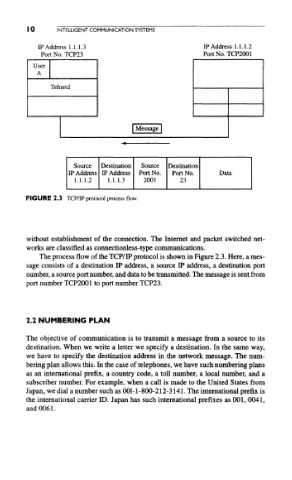
FIGURE 2.3 TCP/IP protocol process flow.
without establishment of the connection. The Internet and packet switched net-
works are classified as connectionless-type communications.
The process flow of the TCP/IP protocol is shown in Figure 2.3. Here, a mes-
sage consists of a destination IP address, a source IP address, a destination port
number, a source port number, and data to be transmitted. The message is sent from
port number TCP2001 to port number TCP23.
2.2 NUMBERING PLAN
The objective of communication is to transmit a message from a source to its
destination. When we write a letter we specify a destination. In the same way,
we have to specify the destination address in the network message. The num-
bering plan allows this. In the case of telephones, we have such numbering plans
as an international prefix, a country code, a toll number, a local number, and a
subscriber number. For example, when a call is made to the United States from
Japan, we dial a number such as 001-1-800-212-3141. The international prefix is
the international carrier ID. Japan has such international prefixes as 001, 0041,
and 0061.