Page 37 - Intelligent Communication Systems
P. 37
CHAPTER 3 / COMMUNICATION NETWORK STRUCTURE 2 1
The transport layer provides end-to-end communication between adjacent
application programs. It decomposes the data transferred from the application layer
and creates the TP (Transport Protocol) packet, attached with the control infor-
mation, such as a program identifier. Then it transfers the TP packet to the Internet
layer.
The Internet layer provides the communication functions between a source
computer and its destination one. It receives a TP packet and the destination IP
address. Then it constructs the IP datagram using the TP packet and the destina-
tion IP address. Using the routing algorithm, it decides the destination computer
or the gateway processor and transfers the IP datagram to the network interface
layer.
The network interface layer provides the control and interface functions for
transmitting the IP datagram through the physical layer. To achieve this, it creates
an HDLC frame or LAN frame, depending on the physical network structure.
When the physical layer is a LAN structure, it corresponds to a device driver
or LAN interfacer. When it is a public network, such as the packet switched net-
work, it corresponds to the communication equipment based on the X.25 standard.
TCP/IP has been implemented by clients independent of OSI activities.
Therefore, it does not match the OSI structure. Basically, the application layer cor-
responds to OSI layers 5 to 7. The transport layer corresponds to OSI layer 4. The
internet layer is like OSI layer 3. The network layer corresponds to OSI layer 2.
The physical layer is like OSI layer 1.
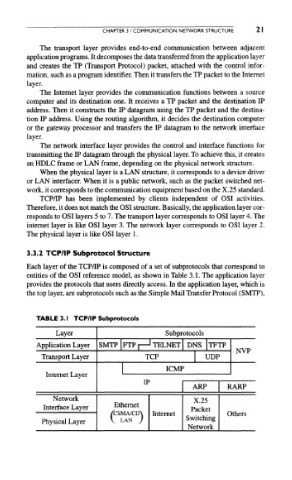
3.3.2 TCP/IP Subprotocol Structure
Each layer of the TCP/IP is composed of a set of subprotocols that correspond to
entities of the OSI reference model, as shown in Table 3.1. The application layer
provides the protocols that users directly access. In the application layer, which is
the top layer, are subprotocols such as the Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP),
TABLE 3.1 TCP/IP Subprotocols