Page 69 - Intelligent Communication Systems
P. 69
CHAPTER 7/NEWLY DEVELOPED TELECOMMUNICATION SERVICES 53
73 CALL FORWARDING SERVICE
Figure 9.12 presents an example of call forwarding service: Terminal A calls termi-
nal B» which is busy, so the call is forwarded to terminal D. Terminal D is predesig-
nated as the terminal to which a call is transferred should the called terminal be busy.
Another service has a call transferred to a phone that has been predesignated as a for-
warding terminal when a call is not responded to within a specified time. This might
be useful, for example, at a small office when staff is away on business.
7.4 CALL WAITING SERVICE
Figure 9.11 shows an example of call waiting service: Terminal A calls terminal
B, which is busy, connected to terminal C. So a signal is sent to terminal B inform-
ing it of the arrival of a second call. If the called party would like to take the call
from terminal A, he or she clicks the phone, picks up the second call, and talks with
caller A while caller C is put on hold.
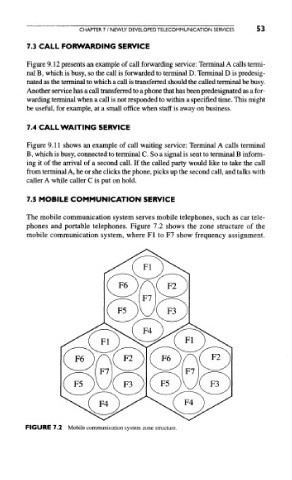
7.5 MOBILE COMMUNICATION SERVICE
The mobile communication system serves mobile telephones, such as car tele-
phones and portable telephones. Figure 7.2 shows the zone structure of the
mobile communication system, where Fl to F7 show frequency assignment.
FIGURE 7.2 Mobile communication system zone structure.