Page 83 - Intelligent Communication Systems
P. 83
66 INTELLIGENT COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS
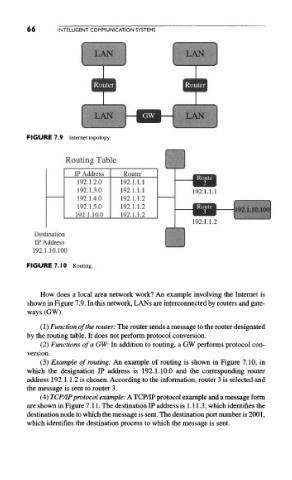
FIGURE 7.9 Internet topology.
FIGURE 7.10 Routing.
How does a local area network work? An example involving the Internet is
shown in Figure 7.9. In this network, LANs are interconnected by routers and gate-
ways (GW),
(1) Function of the router: The router sends a message to the router designated
by the routing table. It does not perform protocol conversion.
(2) Functions of a GW: In addition to routing, a GW performs protocol con-
version.
(3) Example of routing: An example of routing is shown in Figure 7.10, in
which the designation IP address is 192.1.10.0 and the corresponding router
address 192.1.1.2 is chosen. According to the information, router 3 is selected and
the message is sent to router 3.
(4) TCP/IP protocol example: A TCP/IP protocol example and a message form
are shown in Figure 7.11. The destination IP address is 1.11.3, which identifies the
destination node to which the message is sent. The destination port number is 2001,
which identifies the destination process to which the message is sent.