Page 80 - Intelligent Communication Systems
P. 80
CHAPTER 7/NEWLY DEVELOPED TELECOMMUNICATION SERVICES 63
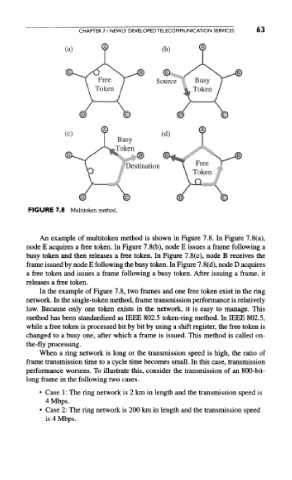
FIGURE 7.8 Multitoken method.
An example of multitoken method is shown in Figure 7.8. In Figure 7.8(a),
node E acquires a free token. In Figure 7.8(b), node E issues a frame following a
busy token and then releases a free token. In Figure 7.8(c), node B receives the
frame issued by node E following the busy token. In Figure 7.8(d), node D acquires
a free token and issues a frame following a busy token. After issuing a frame, it
releases a free token.
In the example of Figure 7.8, two frames and one free token exist in the ring
network. In the single-token method, frame transmission performance is relatively
low. Because only one token exists in the network, it is easy to manage. This
method has been standardized as IEEE 802.5 token-ring method. In IEEE 802.5,
while a free token is processed bit by bit by using a shift register, the free token is
changed to a busy one, after which a frame is issued. This method is called on-
the-fly processing.
When a ring network is long or the transmission speed is high, the ratio of
frame transmission time to a cycle time becomes small. In this case, transmission
performance worsens. To illustrate this, consider the transmission of an 800-bit-
long frame in the following two cases.
• Case 1: The ring network is 2 km in length and the transmission speed is
4 Mbps.
• Case 2: The ring network is 200 km in length and the transmission speed
is 4 Mbps.