Page 389 - Intro Predictive Maintenance
P. 389
380 An Introduction to Predictive Maintenance
mance or continue to plod along as they always have. As a supervisor or manager, it
is in your best interest, as well as your duty, to provide the leadership and motivation
that your workforce needs to achieve and sustain best practices and world-class
performance.
16.2.4 Record Keeping
The foundation records for preventive maintenance are the equipment files. The equip-
ment records provide information for purposes other than preventive maintenance.
The essential items include:
• Equipment identification number
• Equipment name
• Equipment product/group/class
• Location
• Use meter reading
• Preventive maintenance interval(s)
• Use per day
• Last preventive maintenance due
• Next preventive maintenance due
• Cycle time for preventive maintenance
• Crafts required, number of persons, and time for each
• Parts required
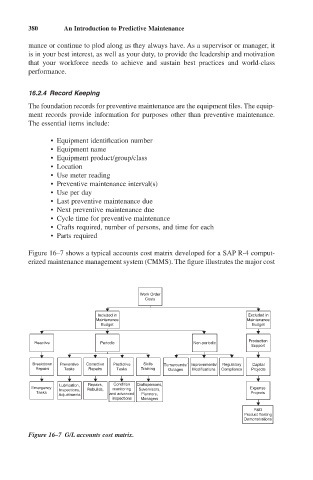
Figure 16–7 shows a typical accounts cost matrix developed for a SAP R-4 comput-
erized maintenance management system (CMMS). The figure illustrates the major cost
Work Order
Costs
Included in Excluded in
Maintenance Maintenance
Budget Budget
Production
Reactive Periodic Non-poriodic
Support
Breakdown Preventive Corrective Predictive Skills Turnarounds/ Improvements/ Regulatory Capital
Repairs Tasks Repairs Tasks Training Outages Modifications Compliance Projects
Lubrication, Repairs, Condition Craftspersons,
Emergency Inspections, Rebuilds, monitoring Suvervisors, Expense
Tasks Projects
Adjustments and advanced Planners,
inspections Managers
R&D
Product Testing
Demonstrations
Figure 16–7 G/L accounts cost matrix.