Page 423 - Intro Predictive Maintenance
P. 423
414 An Introduction to Predictive Maintenance
MAINTENANCE
IMPROVEMENT PREVENTIVE CORRECTIVE
(MI) (PM) (CM)
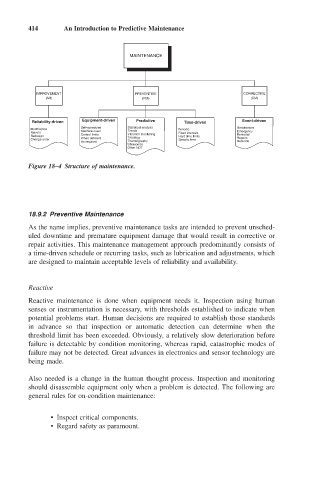
Reliability-driven Equipment-driven Predictive Time-driven Event-driven
Self-scheduled Statistical analysis
Modification Periodic Breakdowns
Retrofit Machine-cued Trends Fixed intervals Emergency
Vibration monitoring
Redesign Control limits Tribology Hard time limits Remedial
Change order When deficient Specific time Repairs
As required Thermography Rebuilds
Ultrasonics
Other NDT
Figure 18–4 Structure of maintenance.
18.9.2 Preventive Maintenance
As the name implies, preventive maintenance tasks are intended to prevent unsched-
uled downtime and premature equipment damage that would result in corrective or
repair activities. This maintenance management approach predominantly consists of
a time-driven schedule or recurring tasks, such as lubrication and adjustments, which
are designed to maintain acceptable levels of reliability and availability.
Reactive
Reactive maintenance is done when equipment needs it. Inspection using human
senses or instrumentation is necessary, with thresholds established to indicate when
potential problems start. Human decisions are required to establish those standards
in advance so that inspection or automatic detection can determine when the
threshold limit has been exceeded. Obviously, a relatively slow deterioration before
failure is detectable by condition monitoring, whereas rapid, catastrophic modes of
failure may not be detected. Great advances in electronics and sensor technology are
being made.
Also needed is a change in the human thought process. Inspection and monitoring
should disassemble equipment only when a problem is detected. The following are
general rules for on-condition maintenance:
• Inspect critical components.
• Regard safety as paramount.