Page 114 - Introduction to AI Robotics
P. 114
3.6 Principles and Issues in Transferring Insights to Robots
fly1 fly2 97
activation
condition
motor schema perceptual schema
snap locate_fly
behavior behavior
percept, percept,
gain gain
motor SI perceptual SI motor SI perceptual SI
snap(fly1) locate_fly(fly1) snap(fly2) locate_fly(fly2)
(x,y,z), (x,y,z),
100% 100%
action, action,
intensity intensity
snap at (x,y,z) snap at (x,y,z)
with all strength with all strength
vector summation:
snaps at the "average"
(x,y,z)
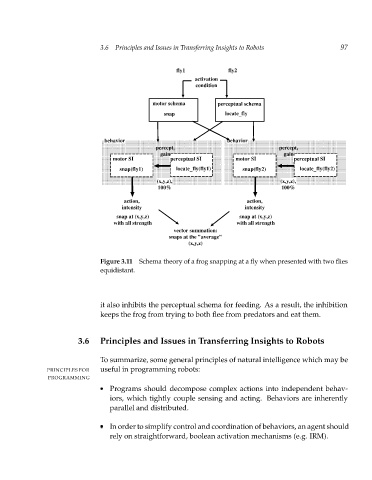
Figure 3.11 Schema theory of a frog snapping at a fly when presented with two flies
equidistant.
it also inhibits the perceptual schema for feeding. As a result, the inhibition
keeps the frog from trying to both flee from predators and eat them.
3.6 Principles and Issues in Transferring Insights to Robots
To summarize, some general principles of natural intelligence which may be
PRINCIPLES FOR useful in programming robots:
PROGRAMMING
Programs should decompose complex actions into independent behav-
iors, which tightly couple sensing and acting. Behaviors are inherently
parallel and distributed.
In order to simplify control and coordination of behaviors, an agent should
rely on straightforward, boolean activation mechanisms (e.g. IRM).