Page 372 - Introduction to AI Robotics
P. 372
355
10.3 Cspace Representations
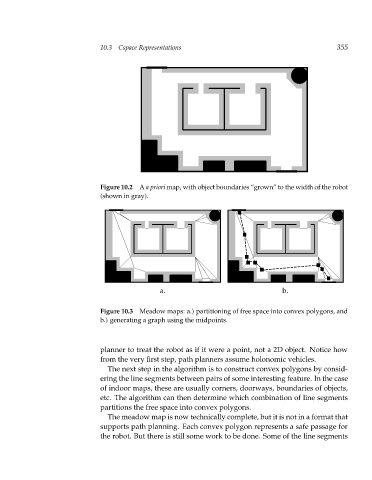
Figure 10.2 A apriori map, with object boundaries “grown” to the width of the robot
(shown in gray).
a. b.
Figure 10.3 Meadow maps: a.) partitioning of free space into convex polygons, and
b.) generating a graph using the midpoints.
planner to treat the robot as if it were a point, not a 2D object. Notice how
from the very first step, path planners assume holonomic vehicles.
The next step in the algorithm is to construct convex polygons by consid-
ering the line segments between pairs of some interesting feature. In the case
of indoor maps, these are usually corners, doorways, boundaries of objects,
etc. The algorithm can then determine which combination of line segments
partitions the free space into convex polygons.
The meadow map is now technically complete, but it is not in a format that
supports path planning. Each convex polygon represents a safe passage for
the robot. But there is still some work to be done. Some of the line segments