Page 376 - Introduction to AI Robotics
P. 376
10.4 Graph Based Planners
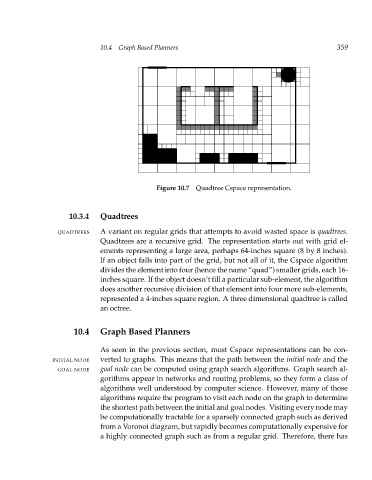
Figure 10.7 Quadtree Cspace representation. 359
10.3.4 Quadtrees
QUADTREES A variant on regular grids that attempts to avoid wasted space is quadtrees.
Quadtrees are a recursive grid. The representation starts out with grid el-
ements representing a large area, perhaps 64-inches square (8 by 8 inches).
If an object falls into part of the grid, but not all of it, the Cspace algorithm
divides the element into four (hence the name “quad”) smaller grids, each 16-
inches square. If the object doesn’t fill a particular sub-element, the algorithm
does another recursive division of that element into four more sub-elements,
represented a 4-inches square region. A three dimensional quadtree is called
an octree.
10.4 Graph Based Planners
As seen in the previous section, most Cspace representations can be con-
INITIAL NODE verted to graphs. This means that the path between the initial node and the
GOAL NODE goal node can be computed using graph search algorithms. Graph search al-
gorithms appear in networks and routing problems, so they form a class of
algorithms well understood by computer science. However, many of those
algorithms require the program to visit each node on the graph to determine
the shortest path between the initial and goal nodes. Visiting every node may
be computationally tractable for a sparsely connected graph such as derived
from a Voronoi diagram, but rapidly becomes computationally expensive for
a highly connected graph such as from a regular grid. Therefore, there has