Page 378 - Introduction to AI Robotics
P. 378
10.4 Graph Based Planners
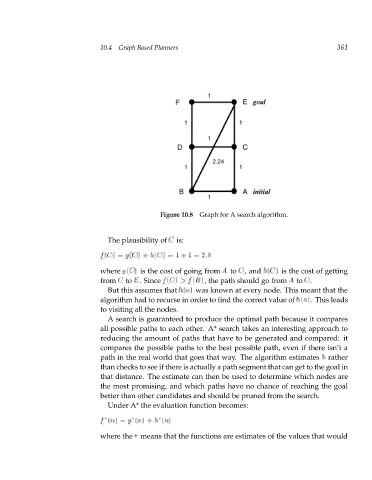
Figure 10.8 Graph for A search algorithm. 361
The plausibility of C is:
f(C) g(C) h(C) = + :0 = 1 + 1 = 2
where g(C) is the cost of going from A to C,and h(C) is the cost of getting
from C to E.Since f(C) > (B), the path should go from A to C f.
But this assumes that h(n) was known at every node. This meant that the
algorithm had to recurse in order to find the correct value of h(n). This leads
to visiting all the nodes.
A search is guaranteed to produce the optimal path because it compares
all possible paths to each other. A* search takes an interesting approach to
reducing the amount of paths that have to be generated and compared: it
compares the possible paths to the best possible path, even if there isn’t a
path in the real world that goes that way. The algorithm estimates h rather
than checks to see if there is actually a path segment that can get to the goal in
that distance. The estimate can then be used to determine which nodes are
the most promising, and which paths have no chance of reaching the goal
better than other candidates and should be pruned from the search.
Under A* the evaluation function becomes:
f (n) g (n) h (n) = +
where the means that the functions are estimates of the values that would