Page 193 - Introduction to Autonomous Mobile Robots
P. 193
178
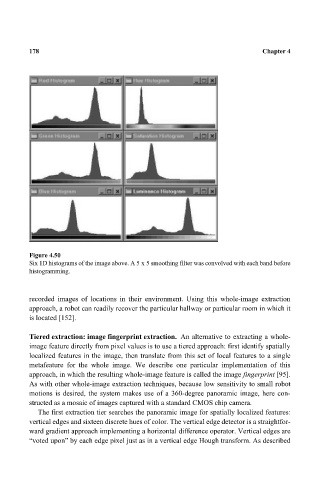
Figure 4.50 Chapter 4
Six 1D histograms of the image above. A 5 x 5 smoothing filter was convolved with each band before
histogramming.
recorded images of locations in their environment. Using this whole-image extraction
approach, a robot can readily recover the particular hallway or particular room in which it
is located [152].
Tiered extraction: image fingerprint extraction. An alternative to extracting a whole-
image feature directly from pixel values is to use a tiered approach: first identify spatially
localized features in the image, then translate from this set of local features to a single
metafeature for the whole image. We describe one particular implementation of this
approach, in which the resulting whole-image feature is called the image fingerprint [95].
As with other whole-image extraction techniques, because low sensitivity to small robot
motions is desired, the system makes use of a 360-degree panoramic image, here con-
structed as a mosaic of images captured with a standard CMOS chip camera.
The first extraction tier searches the panoramic image for spatially localized features:
vertical edges and sixteen discrete hues of color. The vertical edge detector is a straightfor-
ward gradient approach implementing a horizontal difference operator. Vertical edges are
“voted upon” by each edge pixel just as in a vertical edge Hough transform. As described