Page 165 - Introduction to Colloid and Surface Chemistry
P. 165
154 The solid-liquid interface
Adhesional wetting
In adhesional wetting, a liquid which is not originally in contact with
the solid substrate makes contact and adheres to it. In contrast to
spreading wetting, the area of liquid-gas interface decreases. The
work (free energy) of adhesion is given by the Dupre" equation (see
equation (4.29) in the form
= TSG + TLG - TSL (6.7)
which, combined with Young's equation (6.2), gives the Young-
Dupr6 equation,
1.0
15
30
Polytetrafluoroathylene
0.8
(20°C)
45
0.6
60
0.4
75
0.2 1
0 90
-0.2
105
-0.4
10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80
78
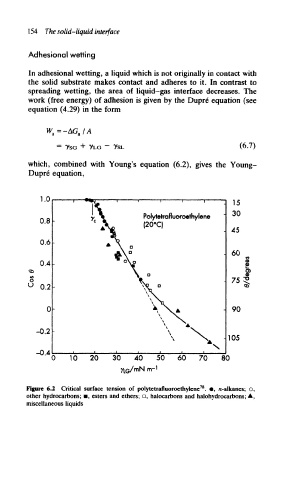
Figure 6.2 Critical surface tension of polytetrafluoroethylene . •, n-alkanes; O,
other hydrocarbons; •, esters and ethers; a, halocarbons and halohydrocarbons; A,
miscellaneous liquids