Page 85 - Introduction to Colloid and Surface Chemistry
P. 85
Liquid-gas and liquid-liquid interfaces 75
1.4
1.5
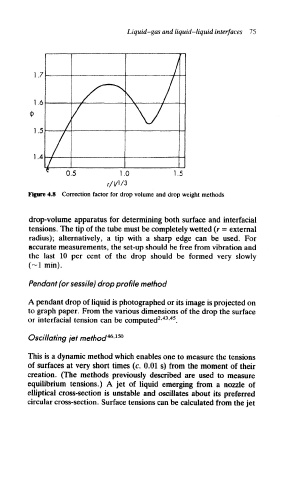
Figure 4.8 Correction factor for drop volume and drop weight methods
drop-volume apparatus for determining both surface and interfacial
tensions. The tip of the tube must be completely wetted (r = external
radius); alternatively, a tip with a sharp edge can be used. For
accurate measurements, the set-up should be free from vibration and
the last 10 per cent of the drop should be formed very slowly
(~1 min).
Pendant (or sessile) drop profile method
A pendant drop of liquid is photographed or its image is projected on
to graph paper. From the various dimensions of the drop the surface
2 43 45
or interfacial tension can be computed ' ' .
46 150
Oscillating jet method -
This is a dynamic method which enables one to measure the tensions
of surfaces at very short times (c. 0.01 s) from the moment of their
creation. (The methods previously described are used to measure
equilibrium tensions.) A jet of liquid emerging from a nozzle of
elliptical cross-section is unstable and oscillates about its preferred
circular cross-section. Surface tensions can be calculated from the jet