Page 126 - Introduction to Electronic Commerce and Social Commerce
P. 126
106 4 Business-to-Business E-Commerce
Intelligent
Collaboration Systems
with Suppliers
and Buyer
Integration Collaboration
2.0
Internal/External
Collaborative Social
Commerce Business
Process Networking
Supply Chain Management
E-Government Improvements RFID and Cloud
Others Computing
Mobile
Personalize Commerce
and Customize Web
e-CRM Services Virtualization
E-Marketplaces
Online Exchanges Intelligent
Ordering e-Learning Systems
Publish B2C, B2B Expert Sales Mobile B2B,
and Promote Auctions Business Value Multichannel Systems Twitter
1 st 2 nd 3 rd 4 th 5 th 6 th
Generation Generation Generation Generation Generation Generation
1995 1997 2000 2001 2002 2010 and Beyond
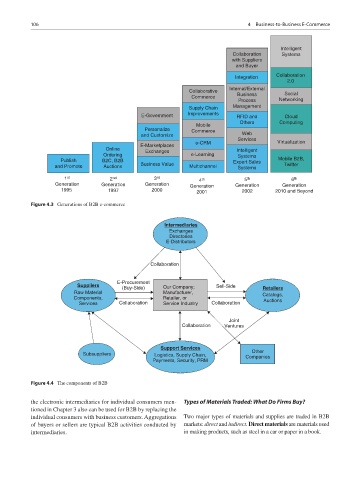
Figure 4.3 Generations of B2B e-commerce
Intermediaries
Exchanges
Directories
E-Distributors
Collaboration
E-Procurement
Suppliers (Buy-Side) Our Company; Sell-Side Retailers
Raw Material Manufacturer, Catalogs,
Components, Retailer, or
Services Collaboration Service Industry Collaboration Auctions
Joint
Collaboration Ventures
Support Services
Other
Subsuppliers Logistics, Supply Chain, Companies
Payments, Security, PRM
Figure 4.4 The components of B2B
the electronic intermediaries for individual consumers men- Types of Materials Traded: What Do Firms Buy?
tioned in Chapter 3 also can be used for B2B by replacing the
individual consumers with business customers. Aggregations Two major types of materials and supplies are traded in B2B
of buyers or sellers are typical B2B activities conducted by markets: direct and indirect. Direct materials are materials used
intermediaries. in making products, such as steel in a car or paper in a book.