Page 140 - Introduction to Electronic Commerce and Social Commerce
P. 140
120 4 Business-to-Business E-Commerce
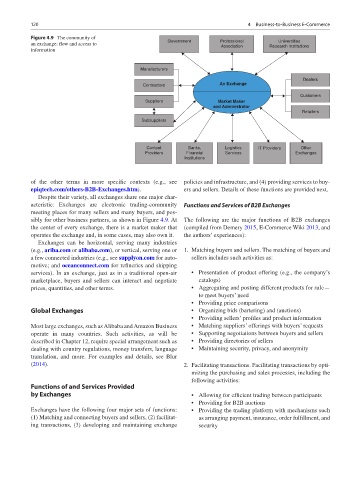
Figure 4.9 The community of Government Professional Universities
an exchange: flow and access to Association Research Institutions
information
Manufacturers
Dealers
Dealers
Contractors An Exchange
Customers
Suppliers Market Maker
and Administrator
Retailers
Subsuppliers
Content Banks, Logistics IT Providers Other
Providers Financial Services Exchanges
Institutions
of the other terms in more specific contexts (e.g., see policies and infrastructure, and (4) providing services to buy-
epiqtech.com/others-B2B-Exchanges.htm). ers and sellers. Details of these functions are provided next.
Despite their variety, all exchanges share one major char-
acteristic: Exchanges are electronic trading-community Functions and Services of B2B Exchanges
meeting places for many sellers and many buyers, and pos-
sibly for other business partners, as shown in Figure 4.9. At The following are the major functions of B2B exchanges
the center of every exchange, there is a market maker that (compiled from Demery 2015, E-Commerce Wiki 2013, and
operates the exchange and, in some cases, may also own it. the authors’ experiences):
Exchanges can be horizontal, serving many industries
(e.g., ariba.com or alibaba.com), or vertical, serving one or 1. Matching buyers and sellers. The matching of buyers and
a few connected industries (e.g., see supplyon.com for auto- sellers includes such activities as:
motive; and oceanconnect.com for refineries and shipping
services). In an exchange, just as in a traditional open-air • Presentation of product offering (e.g., the company’s
marketplace, buyers and sellers can interact and negotiate catalogs)
prices, quantities, and other terms. • Aggregating and posting different products for sale—
to meet buyers’ need
• Providing price comparisons
Global Exchanges • Organizing bids (bartering) and (auctions)
• Providing sellers’ profiles and product information
Most large exchanges, such as Alibaba and Amazon Business • Matching suppliers’ offerings with buyers’ requests
operate in many countries. Such activities, as will be • Supporting negotiations between buyers and sellers
described in Chapter 12, require special arrangement such as • Providing directories of sellers
dealing with country regulations, money transfers, language • Maintaining security, privacy, and anonymity
translation, and more. For examples and details, see Blur
(2014). 2. Facilitating transactions. Facilitating transactions by opti-
mizing the purchasing and sales processes, including the
following activities:
Functions of and Services Provided
by Exchanges • Allowing for efficient trading between participants
• Providing for B2B auctions
Exchanges have the following four major sets of functions: • Providing the trading platform with mechanisms such
(1) Matching and connecting buyers and sellers, (2) facilitat- as arranging payment, insurance, order fulfillment, and
ing transactions, (3) developing and maintaining exchange security