Page 163 - Introduction to Electronic Commerce and Social Commerce
P. 163
144 5 Innovative EC Systems: From E-Government to E-Learning, Knowledge Management, E-Health, and C2C Commerce
4. Describe how e-voting works. people.howstuffworks.com/elearning1.htm, en.wikipedia.
5. Describe the two main areas of G2B activities. org/wiki/E-learning, and webopedia.com/TERM/E/e_
6. How does government use EC internally and when deal- learning.html).
ing with other governments? E-learning is broader than the term online learning,
7. Describe e-government social networking activities. What which generally refers exclusively to Web-based learning.
are some potential benefits? E-learning includes m-learning (or mobile learning) that is
8. Describe m-government and its implementation issues. used when the material is delivered wirelessly to smart-
phones, tablets, or other mobile devices (description to
follow). E-learning is synonymous with computer-based
5.2 E-LEARNING, E-TRAINING, instruction, computer-based training, online education, and
AND E-BOOKS other terms.
It appears in a variety of electronically supported learning
The topic of e-learning is gaining much attention, especially and teaching activities, ranging from virtual classrooms to
because that even first-rate universities such as MIT, Harvard, mobile conferences. E-learning includes a variety of meth-
and Stanford in the United States and Oxford in the United ods of computer-facilitated learning ranging from self-study
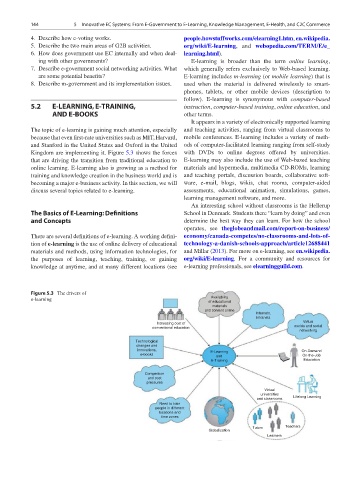
Kingdom are implementing it. Figure 5.3 shows the forces with DVDs to online degrees offered by universities.
that are driving the transition from traditional education to E-learning may also include the use of Web-based teaching
online learning. E-learning also is growing as a method for materials and hypermedia, multimedia CD-ROMs, learning
training and knowledge creation in the business world and is and teaching portals, discussion boards, collaborative soft-
becoming a major e-business activity. In this section, we will ware, e-mail, blogs, wikis, chat rooms, computer-aided
discuss several topics related to e-learning. assessments, educational animation, simulations, games,
learning management software, and more.
An interesting school without classrooms is the Hellerup
The Basics of E-Learning: Definitions School in Denmark. Students there “learn by doing” and even
and Concepts determine the best way they can learn. For how the school
operates, see theglobeandmail.com/report-on- business/
There are several definitions of e-learning. A working defini- economy/canada-competes/no-classrooms-and-lots-of-
tion of e-learning is the use of online delivery of educational technology-a-danish-schools-approach/article12688441
materials and methods, using information technologies, for and Millar (2013). For more on e-learning, see en.wikipedia.
the purposes of learning, teaching, training, or gaining org/wiki/E-learning. For a community and resources for
knowledge at anytime, and at many different locations (see e-learning professionals, see elearningguild.com.
Figure 5.3 The drivers of
e-learning Availability
of educational
materials
and content online
Internets,
intranets
Increasing cost of Virtual
conventional education worlds and social
networking
Technological
changes and
innovations, E-Learning On-Demand
e-books and On-the-Job
E-Training Education
Competition
and cost
pressures
Virtual
universities
and classrooms Lifelong Learning
Need to train
people in different
locations and
time zones
Tutors Teachers
Globalization
Learners