Page 257 - Introduction to Electronic Commerce and Social Commerce
P. 257
242 8 Social Enterprise and Other Social Commerce Topics
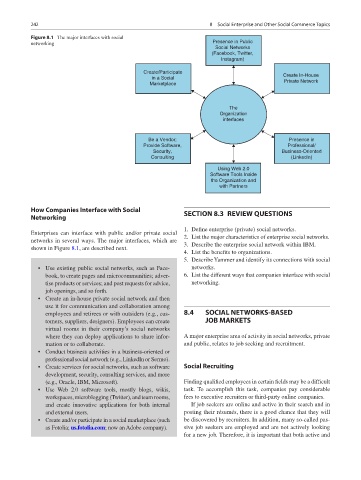
Figure 8.1 The major interfaces with social
networking Presence in Public
Social Networks
(Facebook, Twitter,
Instagram)
Create/Participate
in a Social Create In-House
Marketplace Private Network
The
Organization
interfaces
Be a Vendor; Presence in
Provide Software, Professional/
Security, Business-Oriented
Consulting (Linkedln)
Using Web 2.0
Software Tools Inside
the Organization and
with Partners
How Companies Interface with Social SECTION 8.3 REVIEW QUESTIONS
Networking
1. Define enterprise (private) social networks.
Enterprises can interface with public and/or private social 2. List the major characteristics of enterprise social networks.
networks in several ways. The major interfaces, which are
3. Describe the enterprise social network within IBM.
shown in Figure 8.1, are described next.
4. List the benefits to organizations.
5. Describe Yammer and identify its connections with social
• Use existing public social networks, such as Face- networks.
book, to create pages and microcommunities; adver- 6. List the different ways that companies interface with social
tise products or services; and post requests for advice, networking.
job openings, and so forth.
• Create an in-house private social network and then
use it for communication and collaboration among
employees and retirees or with outsiders (e.g., cus- 8.4 SOCIAL NETWORKS-BASED
tomers, suppliers, designers). Employees can create JOB MARKETS
virtual rooms in their company’s social networks
where they can deploy applications to share infor- A major enterprise area of activity in social networks, private
mation or to collaborate. and public, relates to job seeking and recruitment.
• Conduct business activities in a business-oriented or
professional social network (e.g., LinkedIn or Sermo).
• Create services for social networks, such as software Social Recruiting
development, security, consulting services, and more
(e.g., Oracle, IBM, Microsoft). Finding qualified employees in certain fields may be a difficult
• Use Web 2.0 software tools, mostly blogs, wikis, task. To accomplish this task, companies pay considerable
workspaces, microblogging (Twitter), and team rooms, fees to executive recruiters or third-party online companies.
and create innovative applications for both internal If job seekers are online and active in their search and in
and external users. posting their résumés, there is a good chance that they will
• Create and/or participate in a social marketplace (such be discovered by recruiters. In addition, many so-called pas-
as Fotolia; us.fotolia.com; now an Adobe company). sive job seekers are employed and are not actively looking
for a new job. Therefore, it is important that both active and