Page 277 - Introduction to Electronic Commerce and Social Commerce
P. 277
9.1 Learning About Online Consumer Behavior 263
designed to help vendors understand how a consumer makes dimensions are not controllable by the sellers, while the
a purchasing decision. Through understanding the decision last two are mostly controlled by the sellers. The dimen-
process, a business may be better able to influence the buyer’s sions are shown in Figure 9.1. The influential factors
decision through improved product design or advertising. affect the buyers’ decision process.
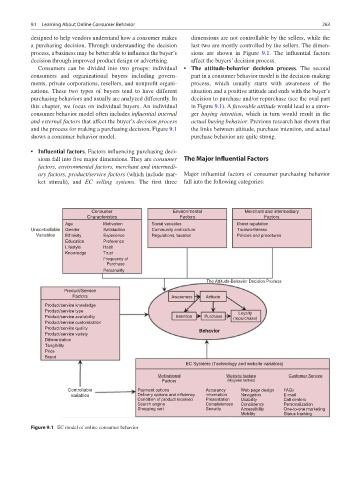
Consumers can be divided into two groups: individual • The attitude-behavior decision process. The second
consumers and organizational buyers including govern- part in a consumer behavior model is the decision-making
ments, private corporations, resellers, and nonprofit organi- process, which usually starts with awareness of the
zations. These two types of buyers tend to have different situation and a positive attitude and ends with the buyer’s
purchasing behaviors and usually are analyzed differently. In decision to purchase and/or repurchase (see the oval part
this chapter, we focus on individual buyers. An individual in Figure 9.1). A favorable attitude would lead to a stron-
consumer behavior model often includes influential internal ger buying intention, which in turn would result in the
and external factors that affect the buyer’s decision process actual buying behavior. Previous research has shown that
and the process for making a purchasing decision. Figure 9.1 the links between attitude, purchase intention, and actual
shows a consumer behavior model. purchase behavior are quite strong.
• Influential factors. Factors influencing purchasing deci-
sions fall into five major dimensions. They are consumer The Major Influential Factors
factors, environmental factors, merchant and intermedi-
ary factors, product/service factors (which include mar- Major influential factors of consumer purchasing behavior
ket stimuli), and EC selling systems. The first three fall into the following categories:
Consumer Environmental Merchant and intermediary
Characteristics Factors Factors
Age Motivation Social variables Brand reputation
Uncontrollable Gender Satisfaction Community and culture Trustworthiness
Variables Ethnicity Experience Regulations, taxation Policies and procetures
Education Preference
Lifestyle Habit
Knowledge Trust
Frequency of
Purchase
Personality
The Attitude-Behavior Decision Process
Product/Service
Factors Awareness Attitude
Product/service knowledge
Product/service type Loyalty
Product/service availability Intention Purchase (repurchase)
Product/service customization
Product/service quality Behavior
Product/service variety
Differentiation
Tangibility
Price
Brand
EC Systems (Technology and website variables)
Motivational Website feature Customer Service
Factors (Hygiene factors)
Controllable Payment options Accurancy Web page design FAQs
variables Delivery options and efficiency Information Navigation E-mail
Condition of product received Presentation Usability Call centers
Search engine Completeness Consistency Personalization
Shopping cart Security Accessibility One-to-one marketing
Mobility Status tracking
Figure 9.1 EC model of online consumer behavior