Page 285 - Introduction to Electronic Commerce and Social Commerce
P. 285
9.4 Web Advertising 271
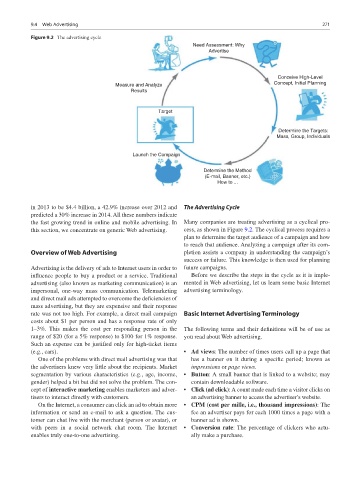
Figure 9.2 The advertising cycle
Need Assessment: Why
Advertise
Conceive High-Level
Measure and Analyze Concept, Initial Planning
Results
Target
Determine the Targets:
Mass, Group, Individuals
Launch the Compaign
Determine the Method
(E-mail, Banner, etc.)
How to ...
in 2013 to be $4.4 billion, a 42.9% increase over 2012 and The Advertising Cycle
predicted a 30% increase in 2014. All these numbers indicate
the fast growing trend in online and mobile advertising. In Many companies are treating advertising as a cyclical pro-
this section, we concentrate on generic Web advertising. cess, as shown in Figure 9.2. The cyclical process requires a
plan to determine the target audience of a campaign and how
to reach that audience. Analyzing a campaign after its com-
Overview of Web Advertising pletion assists a company in understanding the campaign’s
success or failure. This knowledge is then used for planning
Advertising is the delivery of ads to Internet users in order to future campaigns.
influence people to buy a product or a service. Traditional Before we describe the steps in the cycle as it is imple-
advertising (also known as marketing communication) is an mented in Web advertising, let us learn some basic Internet
impersonal, one-way mass communication. Telemarketing advertising terminology.
and direct mail ads attempted to overcome the deficiencies of
mass advertising, but they are expensive and their response
rate was not too high. For example, a direct mail campaign Basic Internet Advertising Terminology
costs about $1 per person and has a response rate of only
1–3%. This makes the cost per responding person in the The following terms and their definitions will be of use as
range of $20 (for a 5% response) to $100 for 1% response. you read about Web advertising.
Such an expense can be justified only for high-ticket items
(e.g., cars). • Ad views: The number of times users call up a page that
One of the problems with direct mail advertising was that has a banner on it during a specific period; known as
the advertisers knew very little about the recipients. Market impressions or page views.
segmentation by various characteristics (e.g., age, income, • Button: A small banner that is linked to a website; may
gender) helped a bit but did not solve the problem. The con- contain downloadable software.
cept of interactive marketing enables marketers and adver- • Click (ad click): A count made each time a visitor clicks on
tisers to interact directly with customers. an advertising banner to access the advertiser’s website.
On the Internet, a consumer can click an ad to obtain more • CPM (cost per mille, i.e., thousand impressions): The
information or send an e-mail to ask a question. The cus- fee an advertiser pays for each 1000 times a page with a
tomer can chat live with the merchant (person or avatar), or banner ad is shown.
with peers in a social network chat room. The Internet • Conversion rate: The percentage of clickers who actu-
enables truly one-to-one advertising. ally make a purchase.