Page 313 - Introduction to Electronic Commerce and Social Commerce
P. 313
300 10 E-Commerce Security and Fraud Issues and Protections
Attacks Targets Defense
Computer
Attackers Information Defenders and Methods
Methods Systems
Software, Regulations,
Hardware, Policy,
Prevention, Strategy,
Intentional Hardware, Detection, Compliance,
criminals, Software, Deterrence Privacy,
Unintentional procedures, (punishments), Protenction,
natural disasters, E-Mail, Remote backup, Cost-benefit,
Malfunctions, Equipment, E-mail defense, Span protection,
Human errors Networks Business Spyware
continuity, protection,
Controls Vulnerability
assessment
People System, Nontechnical
User,
Defense defense
The Legal
Recovery System
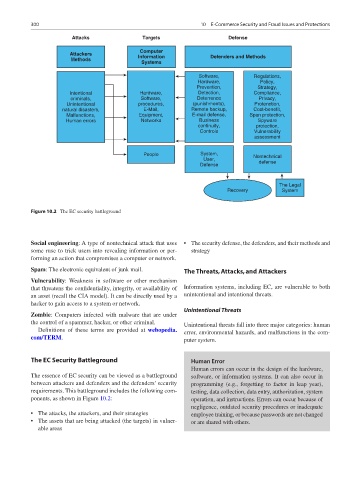
Figure 10.2 The EC security battleground
Social engineering: A type of nontechnical attack that uses • The security defense, the defenders, and their methods and
some ruse to trick users into revealing information or per- strategy
forming an action that compromises a computer or network.
Spam: The electronic equivalent of junk mail. The Threats, Attacks, and Attackers
Vulnerability: Weakness in software or other mechanism
that threatens the confidentiality, integrity, or availability of Information systems, including EC, are vulnerable to both
an asset (recall the CIA model). It can be directly used by a unintentional and intentional threats.
hacker to gain access to a system or network.
Unintentional Threats
Zombie: Computers infected with malware that are under
the control of a spammer, hacker, or other criminal. Unintentional threats fall into three major categories: human
Definitions of these terms are provided at webopedia. error, environmental hazards, and malfunctions in the com-
com/TERM.
puter system.
The EC Security Battleground Human Error
Human errors can occur in the design of the hardware,
The essence of EC security can be viewed as a battleground software, or information systems. It can also occur in
between attackers and defenders and the defenders’ security programming (e.g., forgetting to factor in leap year),
requirements. This battleground includes the following com- testing, data collection, data entry, authorization, system
ponents, as shown in Figure 10.2: operation, and instructions. Errors can occur because of
negligence, outdated security procedures or inadequate
• The attacks, the attackers, and their strategies employee training, or because passwords are not changed
• The assets that are being attacked (the targets) in vulner- or are shared with others.
able areas