Page 308 - Introduction to Electronic Commerce and Social Commerce
P. 308
10.1 The Information Security Problem 295
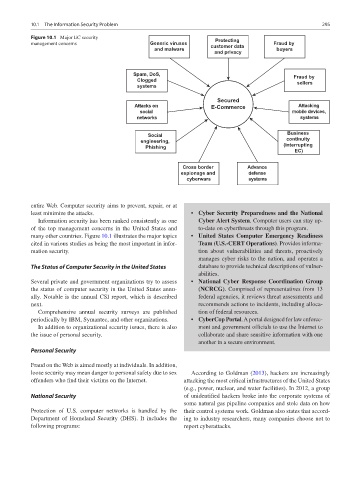
Figure 10.1 Major EC security Protecting
management concerns Generic viruses customer data Fraud by
and malware buyers
and privacy
Spam, DoS, Fraud by
Clogged sellers
systems
Secured
Attacks on E-Commerce Attacking
social mobile devices,
networks systems
Social Business
engineering, continuity
Phishing (interrupting
EC)
Cross border Advance
espionage and defense
cyberwars systems
entire Web. Computer security aims to prevent, repair, or at
least minimize the attacks. • Cyber Security Preparedness and the National
Information security has been ranked consistently as one Cyber Alert System. Computer users can stay up-
of the top management concerns in the United States and to- date on cyberthreats through this program.
many other countries. Figure 10.1 illustrates the major topics • United States Computer Emergency Readiness
cited in various studies as being the most important in infor- Team (U.S.-CERT Operations). Provides informa-
mation security. tion about vulnerabilities and threats, proactively
manages cyber risks to the nation, and operates a
The Status of Computer Security in the United States database to provide technical descriptions of vulner-
abilities.
Several private and government organizations try to assess • National Cyber Response Coordination Group
the status of computer security in the United States annu- (NCRCG). Comprised of representatives from 13
ally. Notable is the annual CSI report, which is described federal agencies, it reviews threat assessments and
next. recommends actions to incidents, including alloca-
Comprehensive annual security surveys are published tion of federal resources.
periodically by IBM, Symantec, and other organizations. • CyberCop Portal. A portal designed for law enforce-
In addition to organizational security issues, there is also ment and government officials to use the Internet to
the issue of personal security. collaborate and share sensitive information with one
another in a secure environment.
Personal Security
Fraud on the Web is aimed mostly at individuals. In addition,
loose security may mean danger to personal safety due to sex According to Goldman (2013), hackers are increasingly
offenders who find their victims on the Internet. attacking the most critical infrastructures of the United States
(e.g., power, nuclear, and water facilities). In 2012, a group
National Security of unidentified hackers broke into the corporate systems of
some natural gas pipeline companies and stole data on how
Protection of U.S. computer networks is handled by the their control systems work. Goldman also states that accord-
Department of Homeland Security (DHS). It includes the ing to industry researchers, many companies choose not to
following programs: report cyberattacks.