Page 320 - Introduction to Electronic Commerce and Social Commerce
P. 320
10.4 Nontechnical Methods: From Phishing to Spam and Fraud 307
and at least one refrigerator, occurred between December 10.4 NONTECHNICAL METHODS:
2013 and January 2014, and was referred to as “the first FROM PHISHING TO SPAM
home appliance ‘botnet’ and the first cyberattack from the AND FRAUD
Internet of Things.” Hackers broke into more than 100,000
home appliances and used them to send over 750,000 mali- As discussed in Section 10.1, there has been a shift to profit-
cious e-mails to enterprises and individuals worldwide (see related Internet crimes. These crimes are conducted with the
Bort 2014). help of both technical methods, such as malicious code that
can access confidential information that may be used to steal
Malvertising money from your online bank account, and nontechnical meth-
ods, such as social engineering.
According to Techopedia, malvertising is “a malicious form
of Internet advertising used to spread malware.” Malvertising
is accomplished by hiding malicious code within relatively Social Engineering and Fraud
safe online advertisements (see techopedia.com/definition/
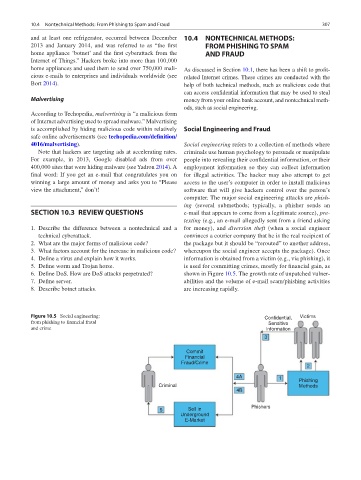
4016/malvertising). Social engineering refers to a collection of methods where
Note that hackers are targeting ads at accelerating rates. criminals use human psychology to persuade or manipulate
For example, in 2013, Google disabled ads from over people into revealing their confidential information, or their
400,000 sites that were hiding malware (see Yadron 2014). A employment information so they can collect information
final word: If you get an e-mail that congratulates you on for illegal activities. The hacker may also attempt to get
winning a large amount of money and asks you to “Please access to the user’s computer in order to install malicious
view the attachment,” don’t! software that will give hackers control over the person’s
computer. The major social engineering attacks are phish-
ing (several submethods; typically, a phisher sends an
SECTION 10.3 REVIEW QUESTIONS e-mail that appears to come from a legitimate source), pre-
texting (e.g., an e-mail allegedly sent from a friend asking
1. Describe the difference between a nontechnical and a for money), and diversion theft (when a social engineer
technical cyberattack. convinces a courier company that he is the real recipient of
2. What are the major forms of malicious code? the package but it should be “rerouted” to another address,
3. What factors account for the increase in malicious code? whereupon the social engineer accepts the package). Once
4. Define a virus and explain how it works. information is obtained from a victim (e.g., via phishing), it
5. Define worm and Trojan horse. is used for committing crimes, mostly for financial gain, as
6. Define DoS. How are DoS attacks perpetrated? shown in Figure 10.5. The growth rate of unpatched vulner-
7. Define server. abilities and the volume of e-mail scam/phishing activities
8. Describe botnet attacks. are increasing rapidly.
Figure 10.5 Social engineering: Confidential, Victims
from phishing to financial fraud Sensitive
and crime Information
3
Commit
Financial
Fraud/Crime
2
4A 1 Phishing
Criminal Methods
4B
5 Sell in Phishers
Underground
E-Market