Page 353 - Introduction to Electronic Commerce and Social Commerce
P. 353
340 11 Electronic Commerce Payment Systems and Order Fulfillment
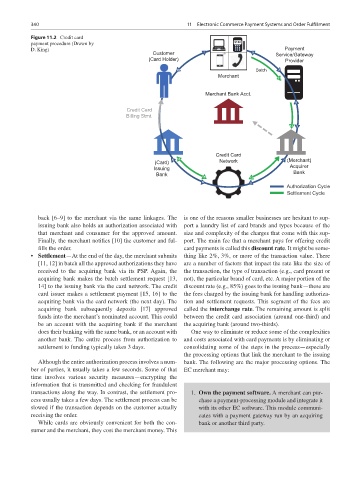
Figure 11.2 Credit card
payment procedure (Drawn by $100
D. King) Payment
Customer 1 9 Service/Gateway
(Card Holder) Provider
10 Batch 2
Merchant
11
Merchant Bank Acct.
8
Credit Card
Billing Stmt.
17
12 3
Credit Card
(Card) 5 14 Network 16 7 (Merchant)
Issuing Acquirer
Bank Bank
15 13
6 4
Authorization Cycle
Settlement Cycle
back [6–9] to the merchant via the same linkages. The is one of the reasons smaller businesses are hesitant to sup-
issuing bank also holds an authorization associated with port a laundry list of card brands and types because of the
that merchant and consumer for the approved amount. size and complexity of the charges that come with this sup-
Finally, the merchant notifies [10] the customer and ful- port. The main fee that a merchant pays for offering credit
fills the order. card payments is called this discount rate. It might be some-
• Settlement—At the end of the day, the merchant submits thing like 2%, 3%, or more of the transaction value. There
[11, 12] in batch all the approved authorizations they have are a number of factors that impact the rate like the size of
received to the acquiring bank via its PSP. Again, the the transaction, the type of transaction (e.g., card present or
acquiring bank makes the batch settlement request [13, not), the particular brand of card, etc. A major portion of the
14] to the issuing bank via the card network. The credit discount rate (e.g., 85%) goes to the issuing bank—these are
card issuer makes a settlement payment [15, 16] to the the fees charged by the issuing bank for handling authoriza-
acquiring bank via the card network (the next day). The tion and settlement requests. This segment of the fees are
acquiring bank subsequently deposits [17] approved called the interchange rate. The remaining amount is split
funds into the merchant’s nominated account. This could between the credit card association (around one-third) and
be an account with the acquiring bank if the merchant the acquiring bank (around two-thirds).
does their banking with the same bank, or an account with One way to eliminate or reduce some of the complexities
another bank. The entire process from authorization to and costs associated with card payments is by eliminating or
settlement to funding typically takes 3 days. consolidating some of the steps in the process—especially
the processing options that link the merchant to the issuing
Although the entire authorization process involves a num- bank. The following are the major processing options. The
ber of parties, it usually takes a few seconds. Some of that EC merchant may:
time involves various security measures—encrypting the
information that is transmitted and checking for fraudulent
transactions along the way. In contrast, the settlement pro- 1. Own the payment software. A merchant can pur-
cess usually takes a few days. The settlement process can be chase a payment-processing module and integrate it
slowed if the transaction depends on the customer actually with its other EC software. This module communi-
receiving the order. cates with a payment gateway run by an acquiring
While cards are obviously convenient for both the con- bank or another third party.
sumer and the merchant, they cost the merchant money. This