Page 93 - Introduction to Electronic Commerce and Social Commerce
P. 93
72 3 Retailing in Electronic Commerce: Products and Services
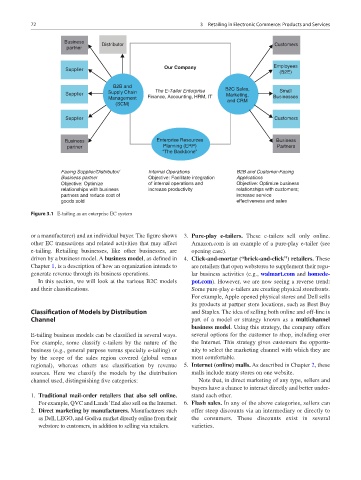
Business Distributor Customers
partner
Supplier Our Company Employees
(B2E)
B2B and B2C Sales,
Supplier Supply Chain The E-Tailer Enterprise Marketing, Small
Management Finance, Accounting, HRM, IT and CRM Businesses
(SCM)
Supplier Customers
Business Enterprise Resources Business
partner Planning (ERP) Partners
“The Backbone”
Facing Supplier/Distributor/ Internal Operations B2B and Customer-Facing
Business partner Objective: Facilitate integration Applications
Objective: Optimize of internal operations and Objective: Optimize business
relationships with business increase productivity relationships with customers;
partners and reduce cost of increase service
goods sold effectiveness and sales
Figure 3.1 E-tailing as an enterprise EC system
or a manufacturer) and an individual buyer. The figure shows 3. Pure-play e-tailers. These e-tailers sell only online.
other EC transactions and related activities that may affect Amazon.com is an example of a pure-play e-tailer (see
e-tailing. Retailing businesses, like other businesses, are opening case).
driven by a business model. A business model, as defined in 4. Click-and-mortar (“brick-and-click”) retailers. These
Chapter 1, is a description of how an organization intends to are retailers that open webstores to supplement their regu-
generate revenue through its business operations. lar business activities (e.g., walmart.com and homede-
In this section, we will look at the various B2C models pot.com). However, we are now seeing a reverse trend:
and their classifications. Some pure-play e-tailers are creating physical storefronts.
For example, Apple opened physical stores and Dell sells
its products at partner store locations, such as Best Buy
Classification of Models by Distribution and Staples. The idea of selling both online and off-line is
Channel part of a model or strategy known as a multichannel
business model. Using this strategy, the company offers
E-tailing business models can be classified in several ways. several options for the customer to shop, including over
For example, some classify e-tailers by the nature of the the Internet. This strategy gives customers the opportu-
business (e.g., general purpose versus specialty e-tailing) or nity to select the marketing channel with which they are
by the scope of the sales region covered (global versus most comfortable.
regional), whereas others use classification by revenue 5. Internet (online) malls. As described in Chapter 2, these
sources. Here we classify the models by the distribution malls include many stores on one website.
channel used, distinguishing five categories: Note that, in direct marketing of any type, sellers and
buyers have a chance to interact directly and better under-
1. Traditional mail-order retailers that also sell online. stand each other.
For example, QVC and Lands’ End also sell on the Internet. 6. Flash sales. In any of the above categories, sellers can
2. Direct marketing by manufacturers. Manufacturers such offer steep discounts via an intermediary or directly to
as Dell, LEGO, and Godiva market directly online from their the consumers. These discounts exist in several
webstore to customers, in addition to selling via retailers. varieties.