Page 135 - Introduction to Information Optics
P. 135
120 2. Signal Processing with Optics
Photorefractive
midium
A3
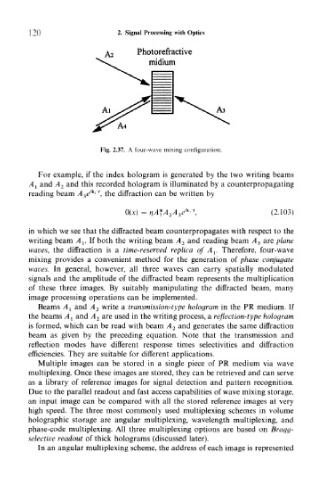
Fig. 2.37. A four-wave mixing configuration.
For example, if the index hologram is generated by the two writing beams
A! and A 2 and this recorded hologram is illuminated by a counterpropagating
k2
reading beam A 3e' \ the diffraction can be written by
0(x) = (2.103)
in which we see that the diffracted beam counterpropagates with respect to the
writing beam A v If both the writing beam A 2 and reading beam A 3 are plane
waves, the diffraction is a time-reserved replica of A l. Therefore, four-wave
mixing provides a convenient method for the generation of phase conjugate
waves. In general, however, all three waves can carry spatially modulated
signals and the amplitude of the diffracted beam represents the multiplication
of these three images. By suitably manipulating the diffracted beam, many
image processing operations can be implemented.
Beams A l and A 2 write a transmission-type hologram in the PR medium. If
the beams A v and A 2 are used in the writing process, a reflection-type hologram
is formed, which can be read with beam A 2 and generates the same diffraction
beam as given by the preceding equation. Note that the transmission and
reflection modes have different response times selectivities and diffraction
efficiencies. They are suitable for different applications.
Multiple images can be stored in a single piece of PR medium via wave
multiplexing. Once these images are stored, they can be retrieved and can serve
as a library of reference images for signal detection and pattern recognition.
Due to the parallel readout and fast access capabilities of wave mixing storage,
an input image can be compared with all the stored reference images at very
high speed. The three most commonly used multiplexing schemes in volume
holographic storage are angular multiplexing, wavelength multiplexing, and
phase-code multiplexing. All three multiplexing options are based on Bragg-
selective readout of thick holograms (discussed later).
In an angular multiplexing scheme, the address of each image is represented