Page 153 - Introduction to Information Optics
P. 153
38 2, Signal Processing with Optics
r(x -x' )
2
2
7IW
0 1
2h —
w d
(b)
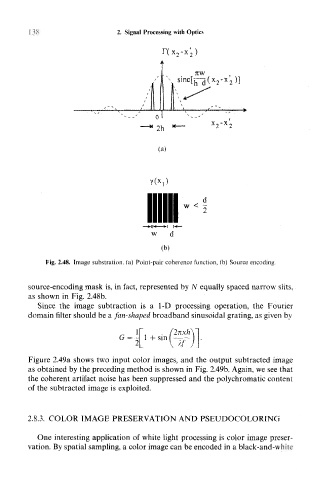
Fig. 2.48. Image substration. (a) Point-pair coherence function, (b) Source encoding.
source-encoding mask is, in fact, represented by N equally spaced narrow slits,
as shown in Fig. 2.48b.
Since the image subtraction is a 1-D processing operation, the Fourier
domain filter should be a fan-shaped broadband sinusoidal grating, as given by
If (2nxh\
G = - 1 + sin —-—
Figure 2.49a shows two input color images, and the output subtracted image
as obtained by the preceding method is shown in Fig. 2.49b. Again, we see that
the coherent artifact noise has been suppressed and the polychromatic content
of the subtracted image is exploited.
2.8.3. COLOR IMAGE PRESERVATION AND PSEUDOCOLORING
One interesting application of white light processing is color image preser-
vation. By spatial sampling, a color image can be encoded in a black-and-white