Page 149 - Introduction to Information Optics
P. 149
134 2. Signal Processing with Optics
Sampling
phase grating
Input
image \
A
(a)
Sampling
phase grating
Input y
image
A
v
L2
(b)
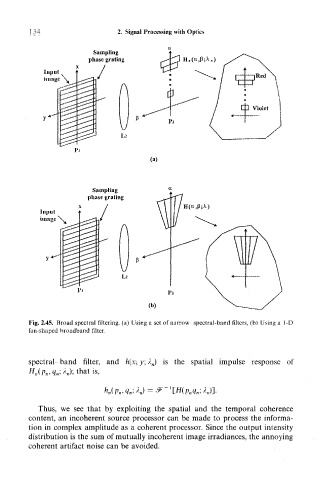
Fig. 2.45. Broad spectral filtering, (a) Using a set of narrow-spectral-band filters, (b) Using a 1-D
fan-shaped broadband filter.
spectral- band filter, and h(x, y; /,„) is the spatial impulse response of
H n (p n,q n ;/-„); that is,
Thus, we see that by exploiting the spatial and the temporal coherence
content, an incoherent source processor can be made to process the informa-
tion in complex amplitude as a coherent processor. Since the output intensity
distribution is the sum of mutually incoherent image irradiances, the annoying
coherent artifact noise can be avoided.