Page 166 - Introduction to Information Optics
P. 166
Exercises
(a) Draw an analog system diagram to represent this problem.
(b) If #(a, /?) is given by
exp
evaluate f(x, y).
(c) We assume a transparency is inserted at (x, y) domain, for which the
amplitude transmittance is given by
2
- +y }
Calculate the complex wave field impinging on the transparency.
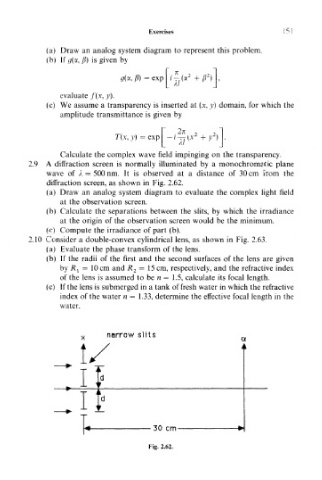
2.9 A diffraction screen is normally illuminated by a monochromatic plane
wave of A = 500 nm. It is observed at a distance of 30 cm from the
diffraction screen, as shown in Fig. 2.62.
(a) Draw an analog system diagram to evaluate the complex light field
at the observation screen.
(b) Calculate the separations between the slits, by which the irradiance
at the origin of the observation screen would be the minimum.
(c) Compute the irradiance of part (b).
2.10 Consider a double-convex cylindrical lens, as shown in Fig. 2.63.
(a) Evaluate the phase transform of the lens.
(b) If the radii of the first and the second surfaces of the lens are given
by R l = 10 cm and R 2 = 15 cm, respectively, and the refractive index
of the lens is assumed to be n — 1.5, calculate its focal length.
(c) If the lens is submerged in a tank of fresh water in which the refractive
index of the water n — 1.33, determine the effective focal length in the
water.
narrow slits
I
30 cm
Fig. 2.62.