Page 440 - Introduction to Information Optics
P. 440
Exercises 425
7.7 Consider the ODJTC as depicted in Fig. 7.59. Assume that the input
function is located behind the joint-transform lens FL2 and also that the
focal length of FL2 is / 2.
(a) Calculate the Fourier spectrum of/(x, y) at the SLM.
(b) To match the quadratic-phase factors of the input and reference OD
function, determine the location of the OD.
(c) Compute the position tolerance of the OD. Assume that m — 10,
SBP - 200, h = 20 mm, and A = 0.5 //m.
7.8 Note that line and continuous tone patterns can be encoded onto the
optical disk in the pit array, thus allowing the enclosed OD patterns to
be addressed in parallel. Assume that the encoding is in binary form.
(a) Describe two encoding techniques for the OD images.
(b) Are the techniques in part (a) suitable for both binary and gray-scale
image patterns? Explain.
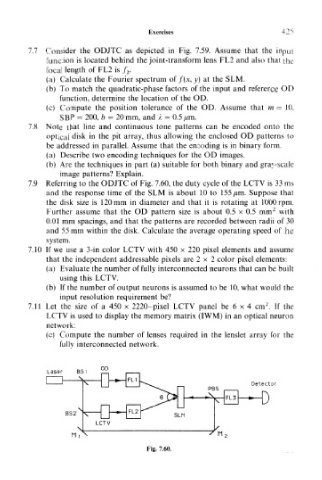
7.9 Referring to the ODJTC of Fig. 7.60, the duty cycle of the LCTV is 33 ms
and the response time of the SLM is about 10 to 155/*m. Suppose that
the disk size is 120mm in diameter and that it is rotating at lOOOrpm.
2
Further assume that the OD pattern size is about 0.5 x 0.5 mm with
0.01 mm spacings, and that the patterns are recorded between radii of 30
and 55 mm within the disk. Calculate the average operating speed of the
system.
7.10 If we use a 3-in color LCTV with 450 x 220 pixel elements and assume
that the independent addressable pixels are 2x 2 color pixel elements:
(a) Evaluate the number of fully interconnected neurons that can be built
using this LCTV.
(b) If the number of output neurons is assumed to be 10, what would the
input resolution requirement be?
2
7.11 Let the size of a 450 x 2220-pixel LCTV panel be 6 x 4 cm . If the
LCTV is used to display the memory matrix (IWM) in an optical neuron
network:
(c) Compute the number of lenses required in the lenslet array for the
fully interconnected network.
Detector
Fig. 7.60.