Page 505 - Introduction to Information Optics
P. 505
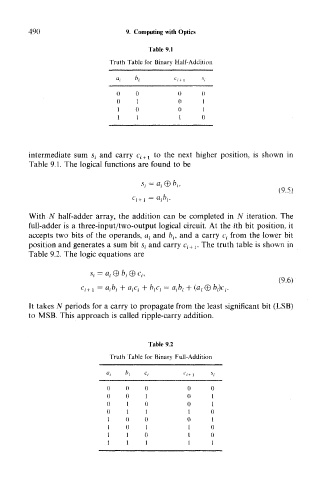
490 9. Computing with Optics
Table 9.1
Truth Table for Binary Half-Addition
intermediate sum s ( and carry c i+1 to the next higher position, is shown in
Table 9.1. The logical functions are found to be
S = fl 0 b;,
(9.5)
With N half-adder array, the addition can be completed in JV iteration. The
full-adder is a three-input/two-output logical circuit. At the ith bit position, it
accepts two bits of the operands, a { and b {, and a carry c t from the lower bit
position and generates a sum bit s { and carry c i+ t . The truth table is shown in
Table 9.2. The logic equations are
s, = a,- 0 h-, © c,.,
(9.6)
c i+i = a ib- l + a tCi + b^ = a ib i + (a i® 6.)c,..
It takes N periods for a carry to propagate from the least significant bit (LSB)
to MSB. This approach is called ripple-carry addition.
Table 9.2
Truth Table for Binary Full-Addition
0 0 0 0 0
0 0 1 0 1
0 1 0 0 1
0 1 1 1 0
1 0 0 0 1
1 0 1 1 0
1 1 0 1 0
1 1 1 1 1