Page 308 - Introduction to Marine Engineering
P. 308
282 Instrumentation and control
section tube formed into a C-shape and sealed at one end. The sealed
end, which is free to move, has a linkage arrangement which will move a
pointer over a scale. The applied pressure acts within the tube entering
through the open end, which is fixed in place. The pressure within the
tube causes it to change in cross section and attempt to straighten out
with a resultant movement of the free end, which registers as a needle
movement on the scale. Other arrangements of the tube in a helical or
spiral form are sometimes used, with the operating principle being the
same.
While the reference or zero value is usually atmospheric, to give gauge
pressure readings, this gauge can be used to read vacuum pressure
values.
Other devices
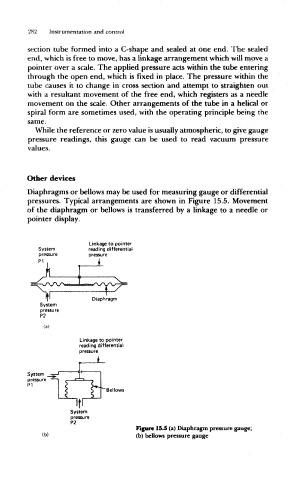
Diaphragms or bellows may be used for measuring gauge or differential
pressures. Typical arrangements are shown in Figure 15.5. Movement
of the diaphragm or bellows is transferred by a linkage to a needle or
pointer display.
Linkage to pointer
reading differential
pressure
i
Diaphragm
(a)
Linkage to pointer
reading differential
pressure
L
Bellows
Figure 15.5 (a) Diaphragm pressure gauge;
(b) (b) bellows pressure gauge