Page 310 - Introduction to Marine Engineering
P. 310
284 Instrumentation and control
Liquid-in-metal thermometer
The use of a metal bulb and capillary bourdon tube filled with liquid
offers advantages of robustness and a wide temperature range. The use
of mercury, for instance, provides a range from —39°C to +650°C. The
bourdon tube may be spiral or helical and on increasing temperature it
tends to straighten. The free end movement is transmitted through
linkages to a pointer moving over a scale.
Bimetallic strip thermometers
A bimetallic strip is made up of two different metals firmly bonded
together. When a temperature change occurs different amounts of
expansion occur in the two metals, causing a bending or twisting of the
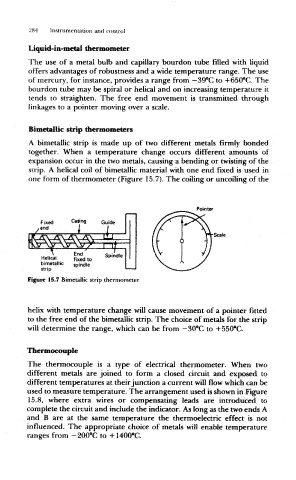
strip. A helical coil of bimetallic material with one end fixed is used in
one form of thermometer (Figure 15.7). The coiling or uncoiling of the
Pointer
Scale
Figure 15.7 Bimetallic strip thermometer
helix with temperature change will cause movement of a pointer fitted
to the free end of the bimetallic strip. The choice of metals for the strip
will determine the range, which can be from — 30°C to +550°C.
Thermocouple
The thermocouple is a type of electrical thermometer. When two
different metals are joined to form a closed circuit and exposed to
different temperatures at their junction a current will flow which can be
used to measure temperature. The arrangement used is shown in Figure
15.8, where extra wires or compensating leads are introduced to
complete the circuit and include the indicator. As long as the two ends A
and B are at the same temperature the thermoelectric effect is not
influenced. The appropriate choice of metals will enable temperature
ranges from ~200°C to +1400°C.