Page 330 - Introduction to Microcontrollers Architecture, Programming, and Interfacing of The Motorola 68HC12
P. 330
10.4 Linked List Structures 307
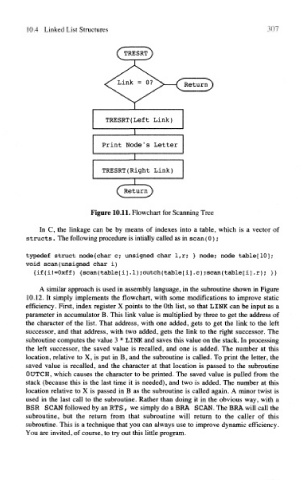
Figure 10.11. Flowchart for Scanning Tree
In C, the linkage can be by means of indexes into a table, which is a vector of
structs. The following procedure is intially called as in scan (0) ;
typedef struct node{char c; unsigned char l,r; } node; node table[10];
void scan(unsigned char i)
{if(i!=0xff) {scan(table[i].l);outch(table[i].c);scan(table[i].r); }}
A similar approach is used in assembly language, in the subroutine shown in Figure
10.12. It simply implements the flowchart, with some modifications to improve static
efficiency. First, index register X points to the Oth list, so that LINK can be input as a
parameter in accumulator B. This link value is multiplied by three to get the address of
the character of the list. That address, with one added, gets to get the link to the left
successor, and that address, with two added, gets the link to the right successor. The
subroutine computes the value 3 * LINK and saves this value on the stack. In processing
the left successor, the saved value is recalled, and one is added. The number at this
location, relative to X, is put in B, and the subroutine is called. To print the letter, the
saved value is recalled, and the character at that location is passed to the subroutine
DUTCH, which causes the character to be printed. The saved value is pulled from the
stack (because this is the last time it is needed), and two is added. The number at this
location relative to X is passed in B as the subroutine is called again. A minor twist is
used in the last call to the subroutine. Rather than doing it in the obvious way, with a
BSR SCAN followed by an RTS, we simply do a BRA SCAN. The BRA will call the
subroutine, but the return from that subroutine will return to the caller of this
subroutine. This is a technique that you can always use to improve dynamic efficiency.
You are invited, of course, to try out this little program.