Page 377 - Introduction to Microcontrollers Architecture, Programming, and Interfacing of The Motorola 68HC12
P. 377
354 Chapter 12 Other Microcontrollers
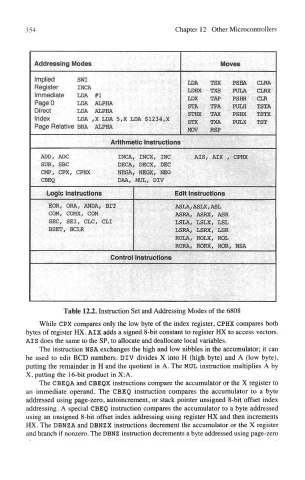
Table 12.2. Instruction Set and Addressing Modes of the 6808
While CPX compares only the low byte of the index register, CPHX compares both
bytes of register HX. AIX adds a signed 8-bit constant to register HX to access vectors.
AIS does the same to the SP, to allocate and deallocate local variables.
The instruction NSA exchanges the high and low nibbles in the accumulator; it can
be used to edit BCD numbers. DIV divides X into H (high byte) and A (low byte),
putting the remainder in H and the quotient in A. The MUL instruction multiplies A by
X, putting the 16-bit product in X:A.
The CBEQA and CBEQX instructions compare the accumulator or the X register to
an immediate operand. The CBEQ instruction compares the accumulator to a byte
addressed using page-zero, autoincrement, or stack pointer unsigned 8-bit offset index
addressing. A special CBEQ instruction compares the accumulator to a byte addressed
using an unsigned 8-bit offset index addressing using register HX and then increments
HX. The DBNZA and DBNZX instructions decrement the accumulator or the X register
and branch if nonzero. The DBNZ instruction decrements a byte addressed using page-zero