Page 167 - Introduction to Paleobiology and The Fossil Record
P. 167
154 INTRODUCTION TO PALEOBIOLOGY AND THE FOSSIL RECORD
(a) Class 1 Effort
Effort
Load
Load
Fulcrum
Fulcrum
Load Effort
Effort
(b) Class 2
Load
Fulcrum
Fulcrum
(c) Class 3
Effort
Load
Fulcrum
Load
Effort Fulcrum
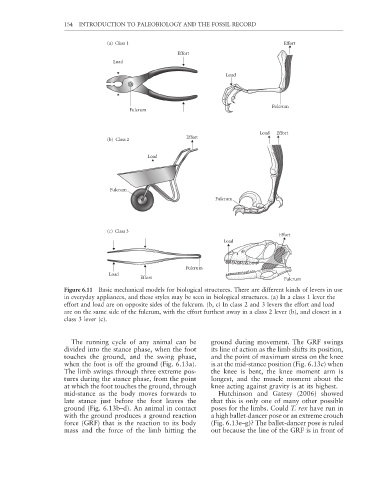
Figure 6.11 Basic mechanical models for biological structures. There are different kinds of levers in use
in everyday appliances, and these styles may be seen in biological structures. (a) In a class 1 lever the
effort and load are on opposite sides of the fulcrum. (b, c) In class 2 and 3 levers the effort and load
are on the same side of the fulcrum, with the effort furthest away in a class 2 lever (b), and closest in a
class 3 lever (c).
The running cycle of any animal can be ground during movement. The GRF swings
divided into the stance phase, when the foot its line of action as the limb shifts its position,
touches the ground, and the swing phase, and the point of maximum stress on the knee
when the foot is off the ground (Fig. 6.13a). is at the mid-stance position (Fig. 6.13c) when
The limb swings through three extreme pos- the knee is bent, the knee moment arm is
tures during the stance phase, from the point longest, and the muscle moment about the
at which the foot touches the ground, through knee acting against gravity is at its highest.
mid-stance as the body moves forwards to Hutchinson and Gatesy (2006) showed
late stance just before the foot leaves the that this is only one of many other possible
ground (Fig. 6.13b–d). An animal in contact poses for the limbs. Could T. rex have run in
with the ground produces a ground reaction a high ballet-dancer pose or an extreme crouch
force (GRF) that is the reaction to its body (Fig. 6.13e–g)? The ballet-dancer pose is ruled
mass and the force of the limb hitting the out because the line of the GRF is in front of