Page 204 - Introduction to Paleobiology and The Fossil Record
P. 204
THE ORIGIN OF LIFE 191
Bacteria Archaea Eucarya
Green non-sulfur Methanosarcina Animals
bacteria Slime
acetivorans Molds
(5.7 Mb)
Gram Halobacterium Fungi
positives Methanobacterium (2.57 Mb)
Purple thermoautotrophicum Plants
bacteria (1.7 Mb)
Archaeoglobus
Methanococcus Ciliates
Cyanobacteria jannaschii fulgidus
Flavobacteria Aeropyrum (1.6 Mb) (2.18 Mb)
pemix Flagellates
(1.6 Mb)
Sulfolobus Trichomonads
solfaticarus
Thermotogales (2.9 Mb)
Microsporidia
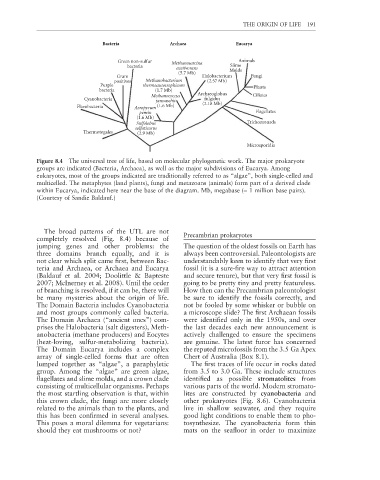
Figure 8.4 The universal tree of life, based on molecular phylogenetic work. The major prokaryote
groups are indicated (Bacteria, Archaea), as well as the major subdivisions of Eucarya. Among
eukaryotes, most of the groups indicated are traditionally referred to as “algae”, both single-celled and
multicelled. The metaphytes (land plants), fungi and metazoans (animals) form part of a derived clade
within Eucarya, indicated here near the base of the diagram. Mb, megabase (= 1 million base pairs).
(Courtesy of Sandie Baldauf.)
The broad patterns of the UTL are not
completely resolved (Fig. 8.4) because of Precambrian prokaryotes
jumping genes and other problems: the The question of the oldest fossils on Earth has
three domains branch equally, and it is always been controversial. Paleontologists are
not clear which split came fi rst, between Bac- understandably keen to identify that very fi rst
teria and Archaea, or Archaea and Eucarya fossil (it is a sure-fire way to attract attention
(Baldauf et al. 2004; Doolittle & Bapteste and secure tenure), but that very fi rst fossil is
2007; McInerney et al. 2008). Until the order going to be pretty tiny and pretty featureless.
of branching is resolved, if it can be, there will How then can the Precambrian paleontologist
be many mysteries about the origin of life. be sure to identify the fossils correctly, and
The Domain Bacteria includes Cyanobacteria not be fooled by some whisker or bubble on
and most groups commonly called bacteria. a microscope slide? The first Archaean fossils
The Domain Archaea (“ancient ones”) com- were identified only in the 1950s, and over
prises the Halobacteria (salt digesters), Meth- the last decades each new announcement is
anobacteria (methane producers) and Eocytes actively challenged to ensure the specimens
(heat-loving, sulfur-metabolizing bacteria). are genuine. The latest furor has concerned
The Domain Eucarya includes a complex the reputed microfossils from the 3.5 Ga Apex
array of single-celled forms that are often Chert of Australia (Box 8.1).
lumped together as “algae”, a paraphyletic The first traces of life occur in rocks dated
group. Among the “algae” are green algae, from 3.5 to 3.0 Ga. These include structures
flagellates and slime molds, and a crown clade identifi ed as possible stromatolites from
consisting of multicellular organisms. Perhaps various parts of the world. Modern stromato-
the most startling observation is that, within lites are constructed by cyanobacteria and
this crown clade, the fungi are more closely other prokaryotes (Fig. 8.6). Cyanobacteria
related to the animals than to the plants, and live in shallow seawater, and they require
this has been confirmed in several analyses. good light conditions to enable them to pho-
This poses a moral dilemma for vegetarians: tosynthesize. The cyanobacteria form thin
should they eat mushrooms or not? mats on the seafloor in order to maximize