Page 209 - Introduction to Paleobiology and The Fossil Record
P. 209
196 INTRODUCTION TO PALEOBIOLOGY AND THE FOSSIL RECORD
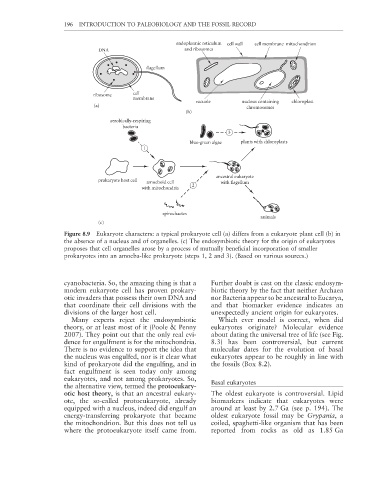
endoplasmic reticulum cell wall cell membrane mitochondrion
DNA and ribosomes
flagellum
ribosome cell
membrane
vacuole nucleus containing chloroplast
(a) chromosomes
(b)
aerobically-respiring
bacteria
3
blue-green algae plants with chloroplasts
1
ancestral eukaryote
prokaryote host cell amoeboid cell with flagellum
2
with mitochondria
spirochaetes
animals
(c)
Figure 8.9 Eukaryote characters: a typical prokaryote cell (a) differs from a eukaryote plant cell (b) in
the absence of a nucleus and of organelles. (c) The endosymbiotic theory for the origin of eukaryotes
proposes that cell organelles arose by a process of mutually beneficial incorporation of smaller
prokaryotes into an amoeba-like prokaryote (steps 1, 2 and 3). (Based on various sources.)
cyanobacteria. So, the amazing thing is that a Further doubt is cast on the classic endosym-
modern eukaryote cell has proven prokary- biotic theory by the fact that neither Archaea
otic invaders that possess their own DNA and nor Bacteria appear to be ancestral to Eucarya,
that coordinate their cell divisions with the and that biomarker evidence indicates an
divisions of the larger host cell. unexpectedly ancient origin for eukaryotes.
Many experts reject the endosymbiotic Which ever model is correct, when did
theory, or at least most of it (Poole & Penny eukaryotes originate? Molecular evidence
2007). They point out that the only real evi- about dating the universal tree of life (see Fig.
dence for engulfment is for the mitochondria. 8.3) has been controversial, but current
There is no evidence to support the idea that molecular dates for the evolution of basal
the nucleus was engulfed, nor is it clear what eukaryotes appear to be roughly in line with
kind of prokaryote did the engulfi ng, and in the fossils (Box 8.2).
fact engulfment is seen today only among
eukaryotes, and not among prokaryotes. So,
the alternative view, termed the protoeukary- Basal eukaryotes
otic host theory, is that an ancestral eukary- The oldest eukaryote is controversial. Lipid
ote, the so-called protoeukaryote, already biomarkers indicate that eukaryotes were
equipped with a nucleus, indeed did engulf an around at least by 2.7 Ga (see p. 194). The
energy-transferring prokaryote that became oldest eukaryote fossil may be Grypania, a
the mitochondrion. But this does not tell us coiled, spaghetti-like organism that has been
where the protoeukaryote itself came from. reported from rocks as old as 1.85 Ga