Page 211 - Introduction to Paleobiology and The Fossil Record
P. 211
198 INTRODUCTION TO PALEOBIOLOGY AND THE FOSSIL RECORD
Era Ma Major events/radiations
Cenozoic
65
Mesozoic Angiosperms Gymnosperms
Floridophycidae Bryophytes
251 Forns
Paleozoic
542 Cryptophytes Stramenopiles Haptophytes Charophytes
Red algae (Cyanidiales) Chlorophytes
Neo
900
Proterozoic Red algae
Glaucophytes
1200
Meso secondary Opisthokonta (animals, fungi)
endosymbiosis
1600
Paleo - primary endosymbiosis CB
3500 Earliest Archaean eubacterial fossil
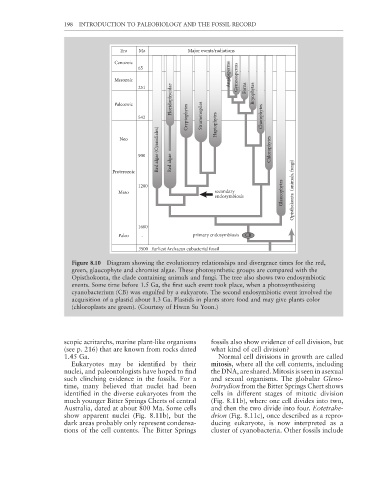
Figure 8.10 Diagram showing the evolutionary relationships and divergence times for the red,
green, glaucophyte and chromist algae. These photosynthetic groups are compared with the
Opisthokonta, the clade containing animals and fungi. The tree also shows two endosymbiotic
events. Some time before 1.5 Ga, the first such event took place, when a photosynthesizing
cyanobacterium (CB) was engulfed by a eukyarote. The second endosymbiotic event involved the
acquisition of a plastid about 1.3 Ga. Plastids in plants store food and may give plants color
(chloroplasts are green). (Courtesy of Hwan Su Yoon.)
scopic acritarchs, marine plant-like organisms fossils also show evidence of cell division, but
(see p. 216) that are known from rocks dated what kind of cell division?
1.45 Ga. Normal cell divisions in growth are called
Eukaryotes may be identifi ed by their mitosis, where all the cell contents, including
nuclei, and paleontologists have hoped to fi nd the DNA, are shared. Mitosis is seen in asexual
such clinching evidence in the fossils. For a and sexual organisms. The globular Gleno-
time, many believed that nuclei had been botrydion from the Bitter Springs Chert shows
identified in the diverse eukaryotes from the cells in different stages of mitotic division
much younger Bitter Springs Cherts of central (Fig. 8.11b), where one cell divides into two,
Australia, dated at about 800 Ma. Some cells and then the two divide into four. Eotetrahe-
show apparent nuclei (Fig. 8.11b), but the drion (Fig. 8.11c), once described as a repro-
dark areas probably only represent condensa- ducing eukaryote, is now interpreted as a
tions of the cell contents. The Bitter Springs cluster of cyanobacteria. Other fossils include