Page 236 - Introduction to Paleobiology and The Fossil Record
P. 236
PROTISTS 223
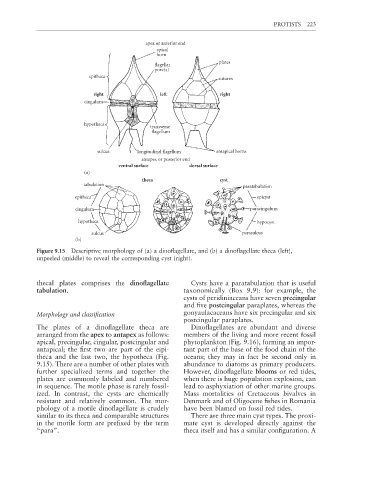
apex or anterior end
apical
horn
plates
flagellar
pore(s)
epitheca
sutures
right left right
cingulum
hypotheca
transverse
flagellum
sulcus longitudinal flagellum antapical horns
antapex or posterior end
ventral surface dorsal surface
(a)
theca cyst
tabulation paratabulation
epitheca epicyst
cingulum paracingulum
hypotheca hypocyst
sulcus parasulcus
(b)
Figure 9.15 Descriptive morphology of (a) a dinoflagellate, and (b) a dinofl agellate theca (left),
unpeeled (middle) to reveal the corresponding cyst (right).
thecal plates comprises the dinofl agellate Cysts have a paratabulation that is useful
tabulation. taxonomically (Box 9.9): for example, the
cysts of peridiniaceans have seven precingular
and fi ve postcingular paraplates, whereas the
Morphology and classifi cation gonyaulacaceans have six precingular and six
postcingular paraplates.
The plates of a dinofl agellate theca are Dinoflagellates are abundant and diverse
arranged from the apex to antapex as follows: members of the living and more recent fossil
apical, precingular, cingular, postcingular and phytoplankton (Fig. 9.16), forming an impor-
antapical; the first two are part of the eipi- tant part of the base of the food chain of the
theca and the last two, the hypotheca (Fig. oceans; they may in fact be second only in
9.15). There are a number of other plates with abundance to diatoms as primary producers.
further specialized terms and together the However, dinofl agellate blooms or red tides,
plates are commonly labeled and numbered when there is huge population explosion, can
in sequence. The motile phase is rarely fossil- lead to asphyxiation of other marine groups.
ized. In contrast, the cysts are chemically Mass mortalities of Cretaceous bivalves in
resistant and relatively common. The mor- Denmark and of Oligocene fi shes in Romania
phology of a motile dinofl agellate is crudely have been blamed on fossil red tides.
similar to its theca and comparable structures There are three main cyst types. The proxi-
in the motile form are prefixed by the term mate cyst is developed directly against the
“para”. theca itself and has a similar confi guration. A