Page 348 - Introduction to Paleobiology and The Fossil Record
P. 348
SPIRALIANS 2: MOLLUSKS 335
dorsal
beak ligament area
cardinal teeth hinge plate
socket
posterior
anterior adductor
adductor scar
scar
anterior
posterior
pallial line pallial sinus
(a) ventral
dorsal
beak
anterior
posterior
ventral
(b)
shell teeth gonad ligament style sac
kidney
heart
posterior
digestive diverticulum
adductor muscle
mouth anus
palp
shell exhalent siphon
anterior inhalent siphon
adductor muscle
position of the gill
(shown in part)
foot
(c)
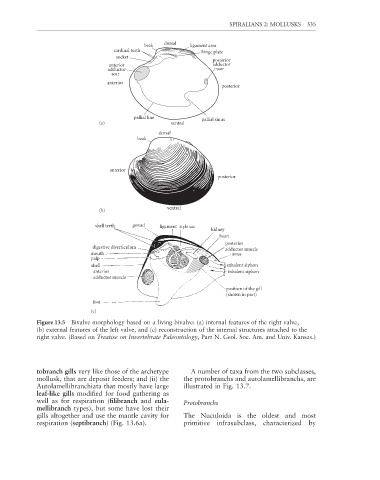
Figure 13.5 Bivalve morphology based on a living bivalve: (a) internal features of the right valve,
(b) external features of the left valve, and (c) reconstruction of the internal structures attached to the
right valve. (Based on Treatise on Invertebrate Paleontology, Part N. Geol. Soc. Am. and Univ. Kansas.)
tobranch gills very like those of the archetype A number of taxa from the two subclasses,
mollusk, that are deposit feeders; and (ii) the the protobranchs and autolamellibranchs, are
Autolamellibranchiata that mostly have large illustrated in Fig. 13.7.
leaf-like gills modified for food gathering as
well as for respiration (fi libranch and eula- Protobranchs
mellibranch types), but some have lost their
gills altogether and use the mantle cavity for The Nuculoida is the oldest and most
respiration (septibranch) (Fig. 13.6a). primitive infrasubclass, characterized by