Page 385 - Introduction to Paleobiology and The Fossil Record
P. 385
372 INTRODUCTION TO PALEOBIOLOGY AND THE FOSSIL RECORD
pelagic – swimming
and floating
molting
mobile
nektobenthos feeding
resting
enrolled molt stage
infaunal – living in burrows
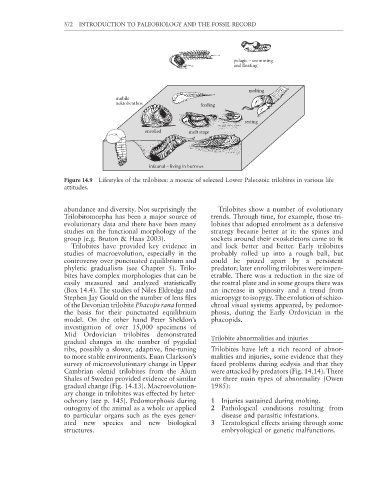
Figure 14.9 Lifestyles of the trilobites: a mosaic of selected Lower Paleozoic trilobites in various life
attitudes.
abundance and diversity. Not surprisingly the Trilobites show a number of evolutionary
Trilobitomorpha has been a major source of trends. Through time, for example, those tri-
evolutionary data and there have been many lobites that adopted enrolment as a defensive
studies on the functional morphology of the strategy became better at it: the spines and
group (e.g. Bruton & Haas 2003). sockets around their exoskeletons came to fi t
Trilobites have provided key evidence in and lock better and better. Early trilobites
studies of macroevolution, especially in the probably rolled up into a rough ball, but
controversy over punctuated equilibrium and could be prized apart by a persistent
phyletic gradualism (see Chapter 5). Trilo- predator; later enrolling trilobites were impen-
bites have complex morphologies that can be etrable. There was a reduction in the size of
easily measured and analyzed statistically the rostral plate and in some groups there was
(Box 14.4). The studies of Niles Eldredge and an increase in spinosity and a trend from
Stephen Jay Gould on the number of lens fi les micropygy to isopygy. The evolution of schizo-
of the Devonian trilobite Phacops rana formed chroal visual systems appeared, by pedomor-
the basis for their punctuated equilibrium phosis, during the Early Ordovician in the
model. On the other hand Peter Sheldon’s phacopids.
investigation of over 15,000 specimens of
Mid Ordovician trilobites demonstrated
gradual changes in the number of pygidial Trilobite abnormalities and injuries
ribs, possibly a slower, adaptive, fi ne-tuning Trilobites have left a rich record of abnor-
to more stable environments. Euan Clarkson’s malities and injuries, some evidence that they
survey of microevolutionary change in Upper faced problems during ecdysis and that they
Cambrian olenid trilobites from the Alum were attacked by predators (Fig. 14.14). There
Shales of Sweden provided evidence of similar are three main types of abnormality (Owen
gradual change (Fig. 14.13). Macroevolution- 1985):
ary change in trilobites was effected by heter-
ochrony (see p. 145). Pedomorphosis during 1 Injuries sustained during molting.
ontogeny of the animal as a whole or applied 2 Pathological conditions resulting from
to particular organs such as the eyes gener- disease and parasitic infestations.
ated new species and new biological 3 Teratological effects arising through some
structures. embryological or genetic malfunctions.