Page 133 - Introduction to Petroleum Engineering
P. 133
120 RESERVOIR GEOPHYSICS
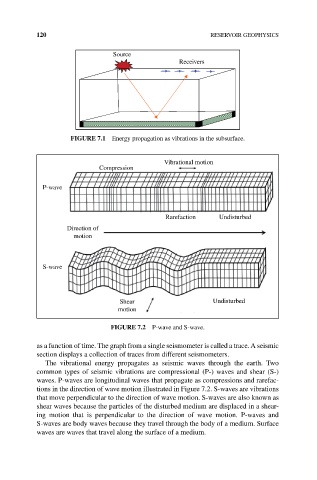
Source
Receivers
FIGuRE 7.1 Energy propagation as vibrations in the subsurface.
Vibrational motion
Compression
P-wave
Rarefaction Undisturbed
Direction of
motion
S-wave
Shear Undisturbed
motion
FIGuRE 7.2 P‐wave and S‐wave.
as a function of time. The graph from a single seismometer is called a trace. A seismic
section displays a collection of traces from different seismometers.
The vibrational energy propagates as seismic waves through the earth. Two
common types of seismic vibrations are compressional (P‐) waves and shear (S‐)
waves. P‐waves are longitudinal waves that propagate as compressions and rarefac-
tions in the direction of wave motion illustrated in Figure 7.2. S‐waves are vibrations
that move perpendicular to the direction of wave motion. S‐waves are also known as
shear waves because the particles of the disturbed medium are displaced in a shear-
ing motion that is perpendicular to the direction of wave motion. P‐waves and
S‐waves are body waves because they travel through the body of a medium. Surface
waves are waves that travel along the surface of a medium.