Page 236 - Introduction to Petroleum Engineering
P. 236
OFFSHORE FACILITIES 223
Crane
Derrick
Helipad
Flare boom
Modules
Jacket
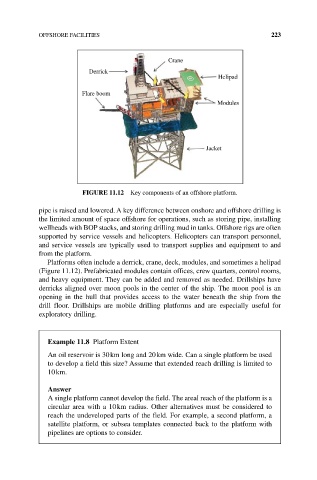
FIgURE 11.12 Key components of an offshore platform.
pipe is raised and lowered. A key difference between onshore and offshore drilling is
the limited amount of space offshore for operations, such as storing pipe, installing
wellheads with BOP stacks, and storing drilling mud in tanks. Offshore rigs are often
supported by service vessels and helicopters. Helicopters can transport personnel,
and service vessels are typically used to transport supplies and equipment to and
from the platform.
Platforms often include a derrick, crane, deck, modules, and sometimes a helipad
(Figure 11.12). Prefabricated modules contain offices, crew quarters, control rooms,
and heavy equipment. They can be added and removed as needed. Drillships have
derricks aligned over moon pools in the center of the ship. The moon pool is an
opening in the hull that provides access to the water beneath the ship from the
drill floor. Drillships are mobile drilling platforms and are especially useful for
exploratory drilling.
Example 11.8 Platform Extent
An oil reservoir is 30 km long and 20 km wide. Can a single platform be used
to develop a field this size? Assume that extended reach drilling is limited to
10 km.
Answer
A single platform cannot develop the field. The areal reach of the platform is a
circular area with a 10 km radius. Other alternatives must be considered to
reach the undeveloped parts of the field. For example, a second platform, a
satellite platform, or subsea templates connected back to the platform with
pipelines are options to consider.