Page 308 - Introduction to Petroleum Engineering
P. 308
THE DOWNSTREAM SECTOR: REFINERIES 297
800
700
Normal boiling point (K) 500
600
400
300
200
100
0
0 5 10 15 20 25 30
Carbon number of normal alkane
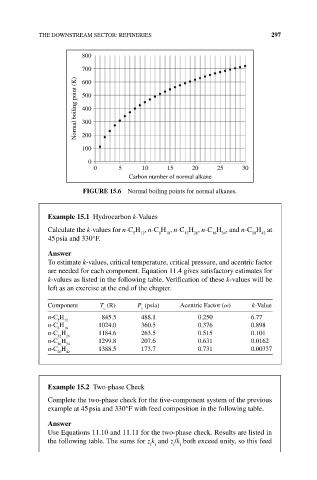
FIguRE 15.6 Normal boiling points for normal alkanes.
Example 15.1 Hydrocarbon k‐Values
Calculate the k‐values for n‐C H , n‐C H , n‐C H , n‐C H , and n‐C H at
8
18
5
12
12
34
16
20
26
42
45 psia and 330°F.
Answer
To estimate k‐values, critical temperature, critical pressure, and acentric factor
are needed for each component. Equation 11.4 gives satisfactory estimates for
k‐values as listed in the following table. Verification of these k‐values will be
left as an exercise at the end of the chapter.
Component T (R) P (psia) Acentric Factor (ω) k‐Value
c c
n‐C H 12 845.5 488.1 0.250 6.77
5
n‐C H 18 1024.0 360.5 0.376 0.898
8
n‐C H 26 1184.6 263.5 0.515 0.101
12
n‐C H 34 1299.8 207.6 0.631 0.0162
16
n‐C H 1388.5 173.7 0.731 0.00337
20 42
Example 15.2 Two‐phase Check
Complete the two‐phase check for the five‐component system of the previous
example at 45 psia and 330°F with feed composition in the following table.
Answer
Use Equations 11.10 and 11.11 for the two‐phase check. Results are listed in
the following table. The sums for z k and z /k both exceed unity, so this feed
i i i i