Page 56 - Introduction to chemical reaction engineering and kinetics
P. 56
38 Chapter 2: Kinetics and Ideal Reactor Models
where U, is the (maximum) velocity at the center of the vessel, and the mean
velocity ii is
ii = u,l2 (2.5-2)
[2] Points (3) and (4) above imply no molecular diffusion in the axial and radial
directions, respectively.
[3] A cylindrical LFR can be pictured physically as consisting of a large number of
thin cylindrical shells (each of thickness dr) of increasing radius (from center to
wall) moving or slipping past each other with decreasing velocity (from center to
wall); the residence time of a thin cylindrical shell at radius r is
t(r) = L/u(r) (2.5-3)
and the mean residence time of all fluid in the vessel is
i = LIE (2.5-4)
= 2t(r)[l - (r/R)2] (2.5-5)
from equations 2.5-1 to -3.
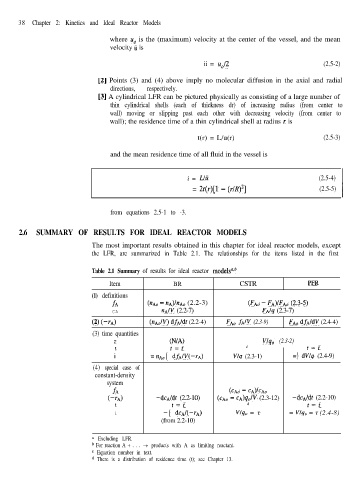
2.6 SUMMARY OF RESULTS FOR IDEAL REACTOR MODELS
The most important results obtained in this chapter for ideal reactor models, except
the LFR, are summarized in Table 2.1. The relationships for the items listed in the first
Table 2.1 Summary of results for ideal reactor modelsGb
Item BR CSTR PFR
(1) definitions
fA (IZA~ - I~A)/~A~ (2.2-3) (FAN -FA)IFAO (2.3-5)
CA nA/v (2.2-7) FA/q (2.3-7)
(2)(--TA) (&&o/V) dfA/dt (2.2-4) FAN fJV (2.3-9) FAN dfA/dV (2.4-4)
(3) time quantities
7 (N/A) V/q, (2.3-2)
t t=i d t=i
i =nAoj dfAIV(-IA) V/q (2.3-1) =\ dV/q (2.4-9)
(4) special case of
constant-density
system
fA (CA0 - CA)ICAo
(-TA) -dcA/dt (2.2-10) (CA0 - cA)q,/V (2.3-12) -dcA/dt (2.2-10)
t t=i d t=i
i = -j dCA/(-TA) v/q, = 7 = V/q, = r (2.4-8)
(from 2.2-10)
0 Excluding LFR.
b For reaction A + . . . + products with A as limiting reactant.
c Equation number in text.
d There is a distribution of residence time (t); see Chapter 13.