Page 118 -
P. 118
Knowledge Capture and Codifi cation 101
Tacit Knowledge Capture
Traditionally, knowledge capture has emphasized the individual ’ s role in gathering
information and creating new knowledge. The literature shows a lack of consensus on
the role of the individual in knowledge acquisition. Some authors (e.g., Nelson and
Winter 1982 ) purport that the fi rm is a learning entity unto itself — that is, it has some
cognitive capabilities that are quite apart from the individuals who comprise it. In
contrast, other authors (e.g., Dodgson 1993 ) do not believe that organizations per se
can acquire knowledge and learn, only individuals can learn. A middle ground is
needed where individuals in the fi rm play a critical role in organizational knowledge
acquisition.
Learning at the individual level, however, is widely accepted to be a fundamentally
social process — something that cannot occur without group interaction in some form.
Individuals thus learn from the collective and at the same time the collective learns
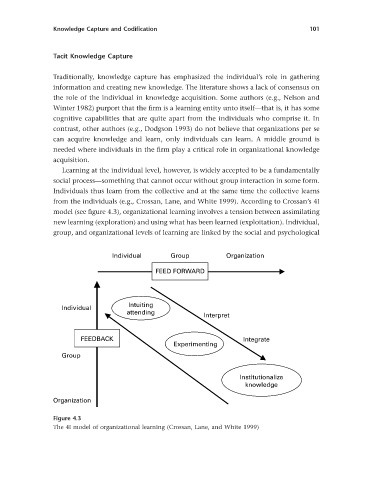
from the individuals (e.g., Crossan, Lane, and White 1999 ). According to Crossan ’ s 4I
model (see fi gure 4.3 ), organizational learning involves a tension between assimilating
new learning (exploration) and using what has been learned (exploitation). Individual,
group, and organizational levels of learning are linked by the social and psychological
Individual Group Organization
FEED FORWARD
Intuiting
Individual
attending Interpret
FEEDBACK Integrate
Experimenting
Group
Institutionalize
knowledge
Organization
Figure 4.3
The 4I model of organizational learning ( Crossan, Lane, and White 1999 )