Page 142 -
P. 142
Knowledge Capture and Codifi cation 125
Plants
Houseplants Landscaping plants Native/wild plants
Ground
Foliage Flowering Trees
cover
Cacti
Deciduous Evergreen
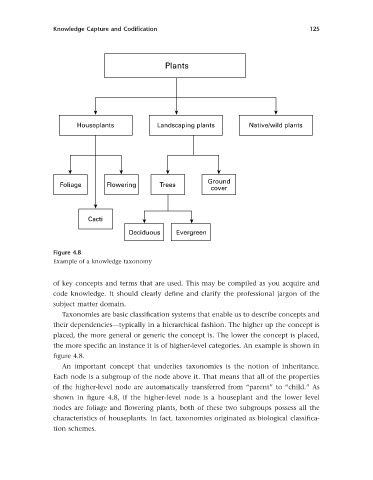
Figure 4.8
Example of a knowledge taxonomy
of key concepts and terms that are used. This may be compiled as you acquire and
code knowledge. It should clearly defi ne and clarify the professional jargon of the
subject matter domain.
Taxonomies are basic classifi cation systems that enable us to describe concepts and
their dependencies — typically in a hierarchical fashion. The higher up the concept is
placed, the more general or generic the concept is. The lower the concept is placed,
the more specifi c an instance it is of higher-level categories. An example is shown in
fi gure 4.8 .
An important concept that underlies taxonomies is the notion of inheritance.
Each node is a subgroup of the node above it. That means that all of the properties
of the higher-level node are automatically transferred from “ parent ” to “ child. ” As
shown in fi gure 4.8 , if the higher-level node is a houseplant and the lower level
nodes are foliage and fl owering plants, both of these two subgroups possess all the
characteristics of houseplants. In fact, taxonomies originated as biological classifi ca-
tion schemes.