Page 132 - Laboratory Manual in Physical Geology
P. 132
Hydrogen
Nitrogen Ash
Carbon
dioxide
Evaporation
of water
Sulphur
dioxide Sediment (sand, mud) and
Water
chemicals dissolved from
rocks transported by
streams
Ash and
cinders Precipitation
of salt
crystals
Ash and Sediment
Lava flow cinders
cools quickly
to tiny crystals
and glass Compaction
of
sediment
Magma
Sedimentary
rock
Magma cools
slowly to large
Igneous crystals
rock
Folding
Fault
Metamorphism
Undeformed
rock layers
Metamorphic not
rock Magma exerts metamorphosed
intense heat and
pressure
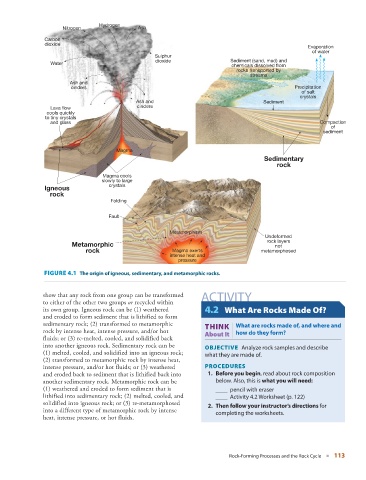
FIGURE 4.1 The origin of igneous, sedimentary, and metamorphic rocks.
show that any rock from one group can be transformed ACTIVITY
to either of the other two groups or recycled within
its own group. Igneous rock can be (1) weathered 4.2 What Are Rocks Made Of?
and eroded to form sediment that is lithified to form
sedimentary rock; (2) transformed to metamorphic THINK What are rocks made of, and where and
rock by intense heat, intense pressure, and/or hot About It
| how do they form?
fluids; or (3) re-melted, cooled, and solidified back
into another igneous rock. Sedimentary rock can be OBJECTIVE Analyze rock samples and describe
(1) melted, cooled, and solidified into an igneous rock; what they are made of.
(2) transformed to metamorphic rock by intense heat,
intense pressure, and/or hot fluids; or (3) weathered PROCEDURES
and eroded back to sediment that is lithified back into 1. Before you begin , read about rock composition
another sedimentary rock. Metamorphic rock can be below. Also, this is what you will need :
(1) weathered and eroded to form sediment that is ____ pencil with eraser
lithified into sedimentary rock; (2) melted, cooled, and ____ Activity 4.2 Worksheet (p. 122 )
solidified into igneous rock; or (3) re-metamorphosed 2. Then follow your instructor’s directions for
into a different type of metamorphic rock by intense completing the worksheets.
heat, intense pressure, or hot fluids.
Rock-Forming Processes and the Rock Cycle ■ 113