Page 133 - Laboratory Manual in Physical Geology
P. 133
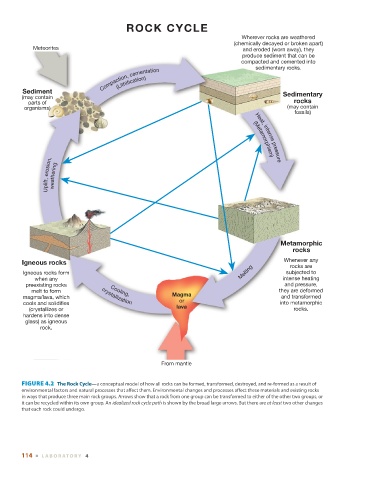
ROCK CYCLE
Wherever rocks are weathered
(chemically decayed or broken apart)
Meteorites and eroded (worn away), they
produce sediment that can be
compacted and cemented into
sedimentary rocks.
Compaction, cementation
(Lithification)
Sediment
(may contain Sedimentary
parts of rocks
organisms) (may contain
fossils)
Heat,
intense
erosion, weathering (Metamorphism) pressure
Uplift,
Metamorphic
rocks
Igneous rocks Whenever any
rocks are
Igneous rocks form Melting subjected to
when any intense heating
preexisting rocks and pressure,
melt to form Cooling, they are deformed
magma/lava, which crystallization Magma and transformed
cools and solidifies or into metamorphic
(crystallizes or lava rocks.
hardens into dense
glass) as igneous
rock.
From mantle
FIGURE 4.2 The Rock Cycle —a conceptual model of how all rocks can be formed, transformed, destroyed, and re-formed as a result of
environmental factors and natural processes that affect them. Environmental changes and processes affect these materials and existing rocks
in ways that produce three main rock groups. Arrows show that a rock from one group can be transformed to either of the other two groups, or
it can be recycled within its own group. An idealized rock cycle path is shown by the broad large arrows. But there are at least two other changes
that each rock could undergo.
114 ■ L ABOR ATORY 4